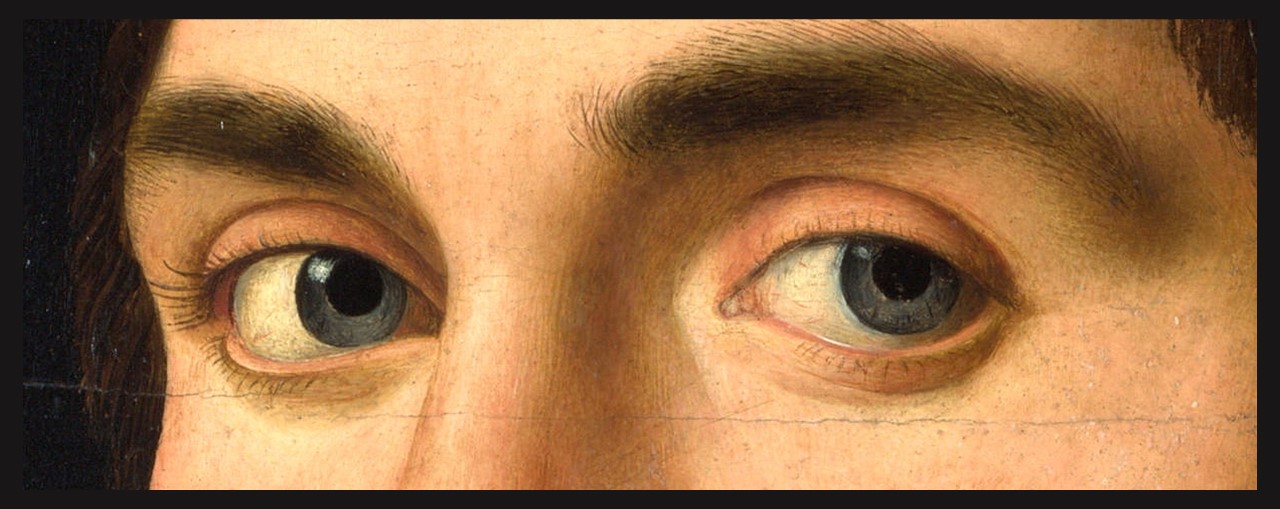
Portrait of a Man (detail), about 1475-6, Oil on poplar, 35.6 x 25.4 cm, National Gallery, London
https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/paintings/antonello-da-messina-portrait-of-a-man
“Now there was one Antonello da Messina, a person of good and lively intelligence, of great sagacity, and skilled in his profession, who, having studied design for many years in Rome, had first retired to Palermo, where he had worked for many years, and finally to his native place, Messina, where he had confirmed by his works the good opinion that his countrymen had of his excellent ability in painting. This man, then, going once on some business of his own from Sicily to Naples, heard that the said King Alfonso had received from Flanders the aforesaid panel by the hand of Johann of Bruges, painted in oil in such a manner that it could be washed, would endure any shock, and was in every way perfect. Thereupon, having contrived to obtain a view of it, he was so strongly impressed by the liveliness of the colours and by the beauty and harmony of that painting, that he put on one side all other business and every thought and went off to Flanders…” Teaching with Antonello da Messina is a set of student activities and worksheets inspired by a very curious Italian artist, a daring creator and an amazing innovator! A few years back in Palermo, in front of his Virgin Annunciate, all I could do was, silently whisper “Ἁγνὴ Παρθένε Δέσποινα, Ἄχραντε Θεοτόκε, Χαῖρε Νύμφη Ἀνύμφευτε. / Παρθένε Μήτηρ Ἄνασσα, Πανένδροσέ τε πόκε, Χαῖρε Νύμφη Ἀνύμφευτε. / Ὑψηλοτέρα οὐρανῶν, ἀκτίνων λαμπροτέρα, Χαῖρε Νύμφη Ἀνύμφευτε. / Χαρὰ Παρθενικῶν Χορῶν, Ἀγγέλων ὑπερτέρα, Χαῖρε Νύμφη Ἀνύμφευτε…” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fiK8wHm4JGM and https://www.saint.gr/236/texts.aspx and http://www.travelingintuscany.com/art/giorgiovasari/lives/antonellodamessina.htm
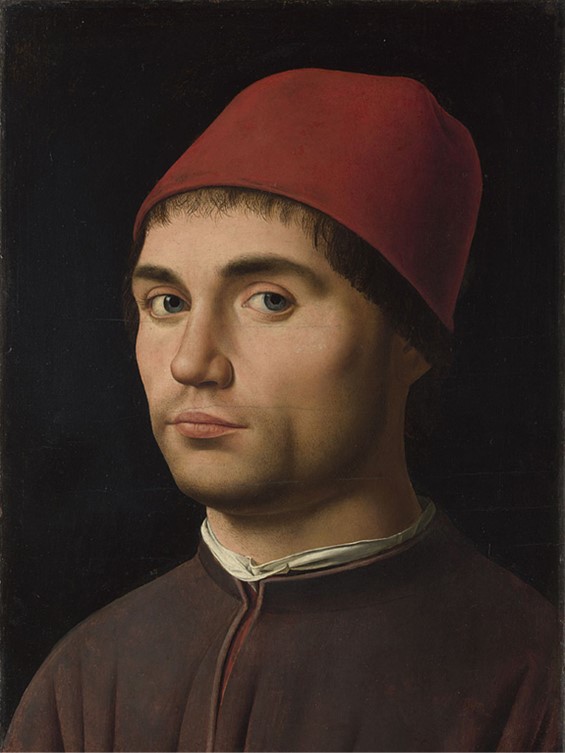

Portrait of a Man, about 1475-6, Oil on poplar, 35.6 x 25.4 cm, National Gallery, London
https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/paintings/antonello-da-messina-portrait-of-a-man
“…Having arrived in Bruges, he became very intimate with the said Johann, making him presents of many drawings in the Italian manner and other things, insomuch that the latter, moved by this and by the respect shown by Antonello, and being now old, was content that he should see his method of colouring in oil; wherefore Antonello did not depart from that place until he had gained a thorough knowledge of that way of colouring, which he desired so greatly to know. And no long time after, Johann having died, Antonello returned from Flanders in order to revisit his native country and to communicate to all Italy a secret so useful, beautiful, and advantageous. Then, having stayed a few months in Messina, he went to Venice, where, being a man much given to pleasure and very licentious, he resolved to take up his abode and finish his life, having found there a mode of living exactly suited to his taste. And so, putting himself to work, he made there many pictures in oil according to the rules that he had learned in Flanders; these are scattered throughout the houses of noblemen in that city, where they were held in great esteem by reason of the novelty of the work. He made many others, also, which were sent to various places. Finally, having acquired fame and great repute there, he was commissioned to paint a panel that was destined for S. Cassiano, a parish church in that city. This panel was wrought by Antonio with all his knowledge and with no sparing of time; and when finished, by reason of the novelty of the colouring and the beauty of the figures, which he had made with good design, it was much commended and held in very great price. And afterwards, when men heard of the new secret that he had brought from Flanders to that city, he was ever loved and cherished by the magnificent noblemen of Venice throughout the whole course of his life…” I think… let Vasari “speak,” he is probably the best to introduce to my students, Antonello da Messina’s contribution to Italian Renaissance Art… http://www.travelingintuscany.com/art/giorgiovasari/lives/antonellodamessina.htm

San Cassiano Altar (detail), 1475-76, Oil on panel, Kunsthistorisches Museum, Vienna
https://artinwords.de/antonello-da-messina-pala-di-san-cassiano-sacra-conversazione/
Teaching with Antonello da Messina References – References, a PowerPoint and Activities…
For a List of ONLINE References on Antonello da Messina TeacherCurator put together, please… Click HERE!
For my PowerPoint on Antonello da Messina, please… Click HERE!
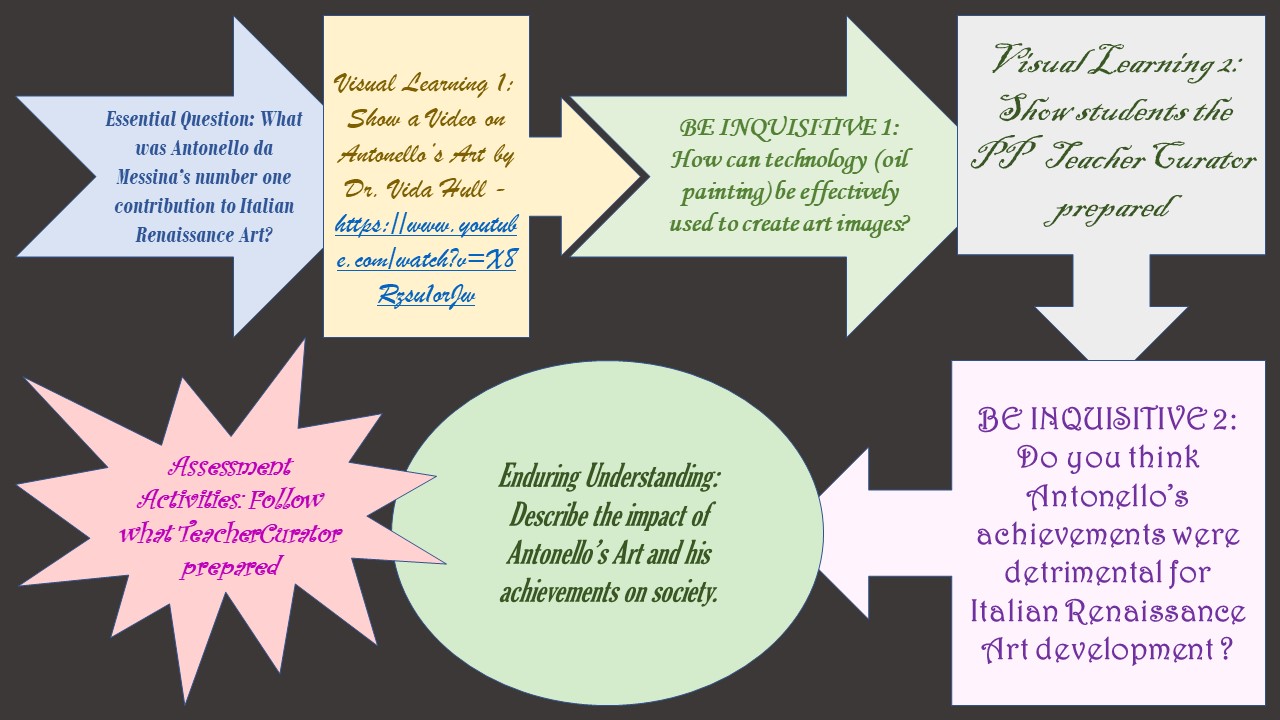
I always feel confident discussing an artist with my students when I prepare my Steps to Success Lesson Plan Outline…
For Student Activities (3 Activities), please… Click HERE!
I hope, Teaching with Antonello da Messina, will prove easy and helpful. Do you think it justifies my BLOG name Teacher Curator?
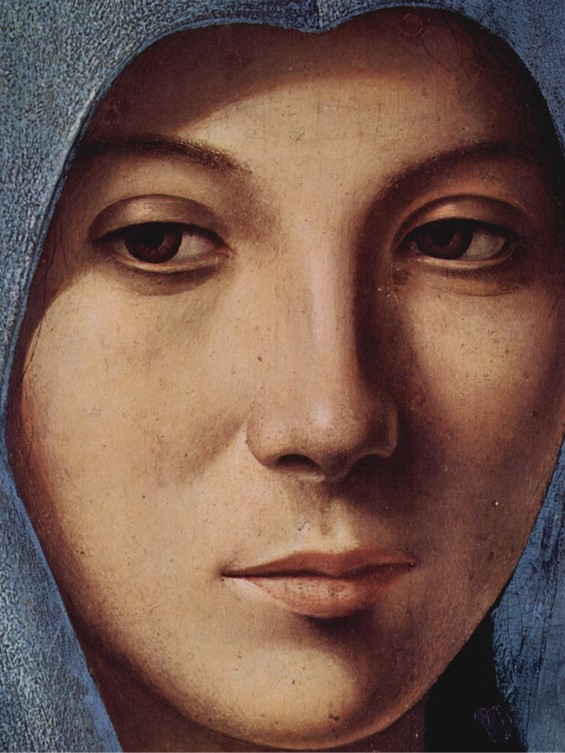

Virgin Annunciate (detail), c. 1476, Oil on wood, 45 x 34,5 cm, Galleria Regionale della Sicilia, Palermo
https://eclecticlight.co/2019/08/02/the-first-italian-master-in-oil-antonello-da-messina-2/