Amarantha sweet and fair / Ah braid no more that shining hair! / As my curious hand or eye / Hovering round thee let it fly. / Let it fly as unconfin’d / As its calm ravisher, the wind, / Who hath left his darling th’East, / To wanton o’er that spicy nest. / Ev’ry tress must be confest / But neatly tangled at the best; / Like a clue of golden thread, / Most excellently ravelled. / Do not then wind up that light / In ribands, and o’er-cloud in night; / Like the sun in’s early ray, / But shake your head and scatter day… wrote Richard Lovelace, back in the 17th century… no Hellenistic Golden Hairnets for… Amarantha sweet and fair! https://www.poetryfoundation.org/poets/richard-lovelace
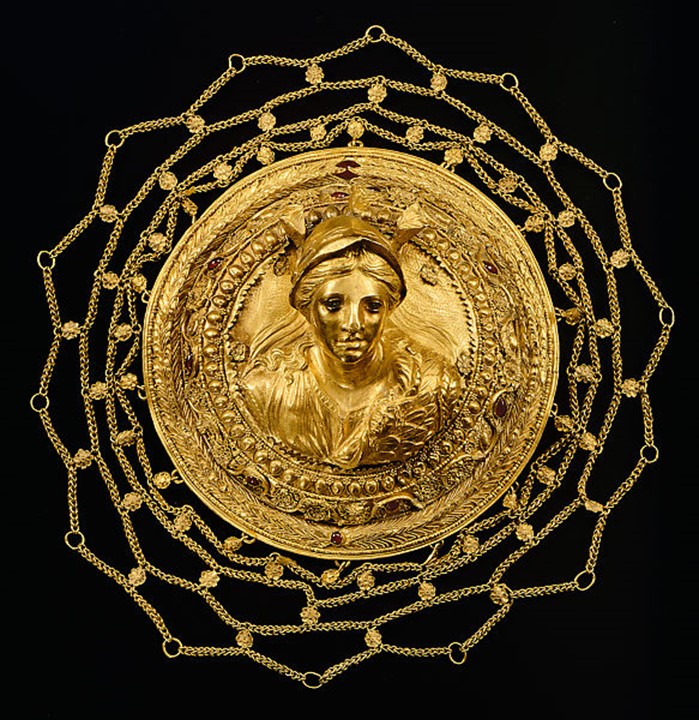

Photo Credit: https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/642596
The visitors of the Ancient Greeks: Science and Wisdom Exhibition in the Science Museum (London, 17 November 2021 – 05 June 2022) will be able to admire a rare, Hellenistic Golden Hairnet from the Benaki Museum in Athens and marvel at its amazing beauty and craftsmanship! This is a real treat as only a handful of such Golden Hairnets survive today scattered around major Museums around the world. https://www.sciencemuseum.org.uk/see-and-do/ancient-greeks-science-and-wisdom
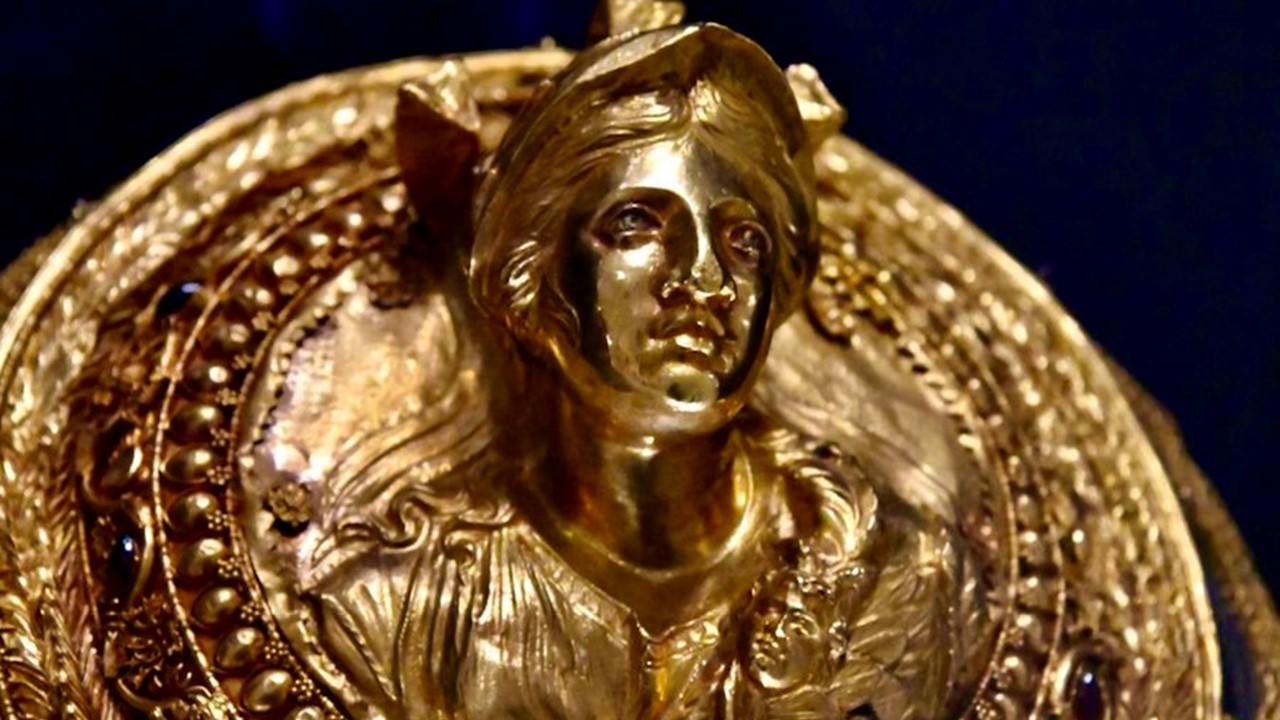
The Exhibited Hairnet comes to London from Greece, and specifically, the Benaki Museum in Athens. Gold Hairnets were created by exceptional goldsmiths for aristocratic, well-to-do Greek ladies of the Hellenistic period (late 4th to early 1st cent. BC), to contain a simple hair chignon at the back of their head. The Benaki Hairnet consists of a central gold medallion with a bust of Athena in high relief, and an intricate, gold net. Goddess Athena is depicted wearing a helmet with three plumes, a laurel wreath, and an oblique aegis with a mermaid. The bust of Athena is framed by concentric bands adorned with ornaments applied in the jeweler’s fine technique of filigree and granulation. The lavish decoration is mostly floral consisting of a wreath of beautifully executed pointed leaves, an exquisite, and complex band of floral designs, and a strip of eggs and tiny rosettes. The central medallion was further embellished with enameling and minuscule beads of garnet. The gold net around the medallion consists of a lattice of chains with intersecting points articulated with tiny rosettes. What an amazing achievement of workmanship! https://www.benaki.org/index.php?option=com_buildings&view=building&id=11&Itemid=533&lang=en and https://www.benaki.org/index.php?option=com_collectionitems&view=collectionitem&id=140287&lang=en&lang=el and https://ellaniapili.blogspot.com/2015/11/blog-post_328.html
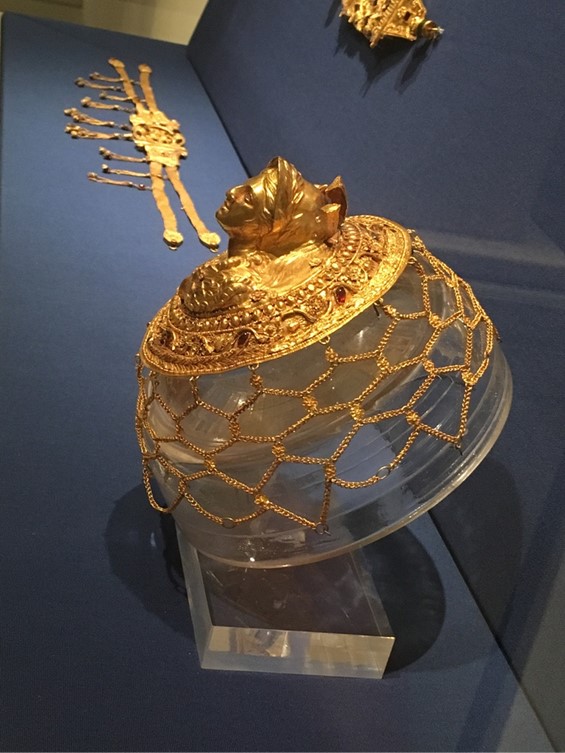

Photo Credit: https://www.myfaveplaces.com/contemp-galleries/2016/7/6/gold-gold-gold-plus-some-bronze-and-silver
Describing the Benaki Museum Medallion Berta Segall writes… The artist of the Benaki medallion wanted to achieve unity. The elements of the ornamental frame are part of a continuous, flowing design, the bust, by taking up as much as possible of the background and touching the border, gives the impression of a full length figure cut off by a wreath. Its modeling is an example of the “impressionistic” technique in relief which uses a soft, almost imperceptible gradation of planes from the high to the very low, and from there to engraving. Thus, the folds of the garment are indicated in low relief, and even shallower, almost disappearing into the background, are the two plumes of the helmet right and left of the face. Berta Segall, Two Hellenistic Gold Medallions from Thessaly, Record of the Museum of Historic Art, Princeton University, Vol. 4, No. 2 (Autumn, 1945), pp. 2-11 https://www.jstor.org/stable/3774132?seq=3#metadata_info_tab_contents
The Benaki Museum Hairnet was part of an unbelievable “treasure” of 44 pieces of jewelry sold to private collectors in Athens, in 1929. The “treasure,” a product of illegal excavations, came from Thessaly, and the exact circumstances of their discovery are not well established. According to one testimony, they were discovered inside a copper vessel near Almyros in Magnesia, according to a source, the “treasure” came from the area of Lamia-Lianokladi. It has also been claimed that the 44 pieces of exquisite jewelry were found in Domokos, while the antique dealer, who sold 35 pieces of jewelry to the collector Eleni Stathatou (today in the Stathatos Collection in the National Archaeological Museum in Athens) and 9 to the Benaki Museum, assured that they were discovered near Karpenisi. https://ellaniapili.blogspot.com/2015/11/blog-post_328.html
For a PowerPoint on Hellenistic Golden Hairnets, please… check HERE!

Photo Credit: https://twitter.com/AngHellenLeague/status/1464252708806873091/photo/1
The Science Museum in London promises a unique experience to the visitors of their free exhibition Ancient Greeks: Science and Wisdom (17 November 2021 – 05 June 2022). The Museum experts believe that curiosity and investigation are central to furthering our understanding of the universe today… and suggest that we step back through millennia… and discover how the ancient Greek civilization questioned, contemplated, and debated the natural world. If your steps take you to London, the Science Museum Exhibition Ancient Greeks: Science and Wisdom, is worth visiting! https://www.sciencemuseum.org.uk/see-and-do/ancient-greeks-science-and-wisdom and https://www.sciencemuseum.org.uk/guides for a free guidebook.