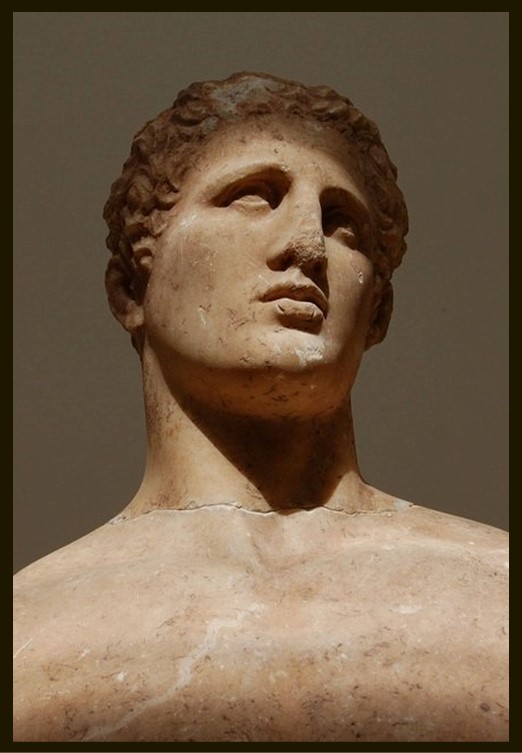
The family offering of Daochos II, or of the House of the Thessalians was initially erected on the prominent terrace northeast of the temple. It comprises a group of marble statues dedicated to Apollo by Daochos II, a Thessalian dignitary from Pharsalus, who represented his people in the Amphictyonic League of Delphi (336-332 BC) where he served the interests of the Macedonians. Nine statues stood on a narrow space: Apollo (lost) and eight representatives of the dedicator’s powerful family (Agias Son of Aknonios is one of them) who were famous for their political, military and athletic exploits. We know the names and glorious deeds of the men represented from the inscriptions carved on the front of the base. Although the figures are deployed in a line and differ from one another in pose and dress, they nevertheless interact through the symmetrical or contrasting movement of their bodies, gestures, and turns of the head. Rosina Colonia, The Archaeological Museum of Delphi, John S. Latsis Public Benefit Foundation, Athens, Greece, page 321 https://www.latsis-foundation.org/content/elib/book_13/delphoi_en.pdf

The monument of Daoxhos II at Delphi, a family portrait gallery of eight statues, showcases six successive generations within the direct family lineage of Daochos II, stretching back to the late 6th century. It starts on the right side of the Monument, with the statue of Apollo (the statue is lost), the deity to whom the monument was dedicated. Based on the size and shallow nature of the carving, it is likely that the statue depicted Apollo in a seated position.
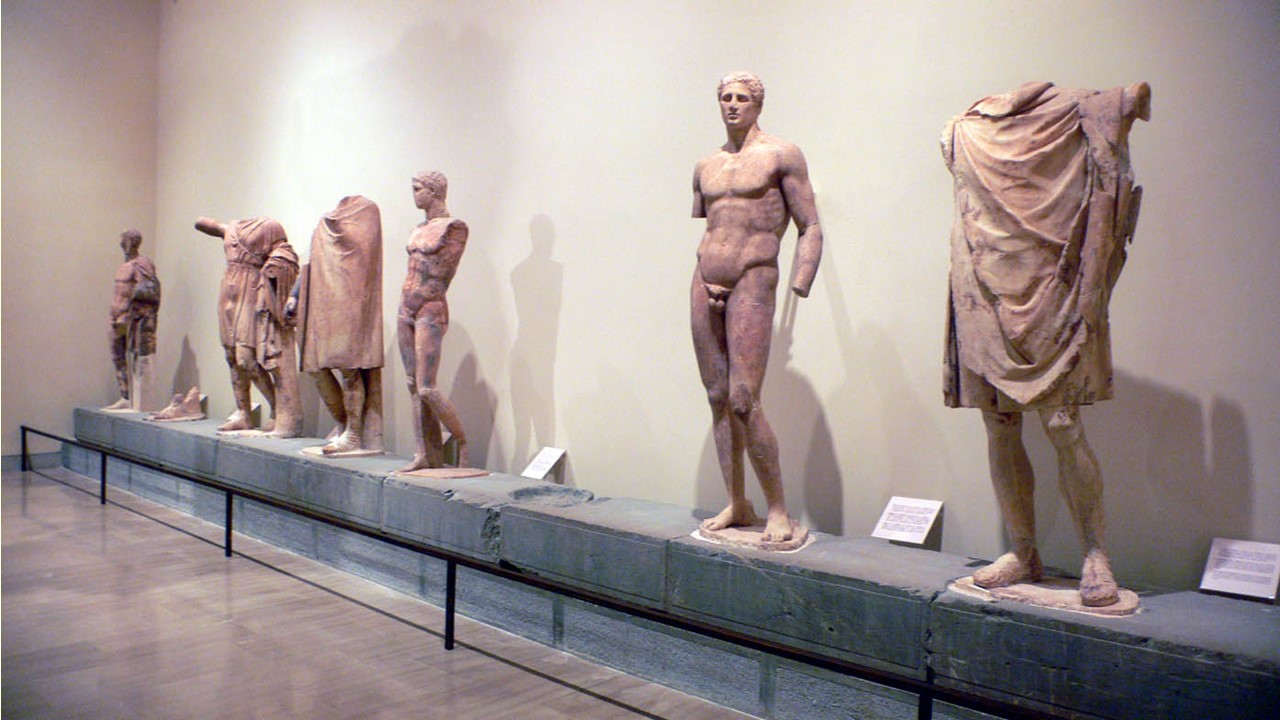

On the right side of Apollo, the unknown artist of the Monument placed the statue of Aknonios, great-great-grandfather of Daochos II, who lived during the Persian Wars and served as Tetrarch of Thessaly. Aknonios is followed by his three sons, all of them distinguished athletes. First comes the oldest son, Agias, the great-grandfather of Daochos II. Placed next to his father following a generational sequence, Agias was a distinguished athlete of Pankration, an Olympian, and the winner of many Panhellenic Games during the 5th century. His brother Telemachos, a 440 BC Olympic Games Wrestling Winner comes next, followed by the younger of the three brothers, Agelaos, a champion Runner. Daochos I, son of Agias, grandfather of the monument’s donor, and Tetrarch of Thessaly for twenty-seven peaceful years are placed next to Agelaos. He is followed by Sisyphus I, his son, a military man, his grandson, and donor, Daochos II, and finally Sisyphus II, the youngest member of the Thessalian family.

The statue of each depicted member of the Thessalian family is differentiated, by pose, anatomy, and dress. Each statue stands alone, yet, their body postures, hand gestures, and the way their heads turn unite them, creating a tight composition. The represented statesmen, for example, Aknonios and Daochos I, depicted wearing the short chlamys favoured by Macedonian and Thessalian men, look sturdy and solemn. Sisyphus I, the only military representative in the Daochos II group, is presented as if he is giving military orders. As for the rest, Agias, Telemachos, Agelaos, and young Sisyphus II, presented in the nude, are perfect examples of youth and athletic prowess.
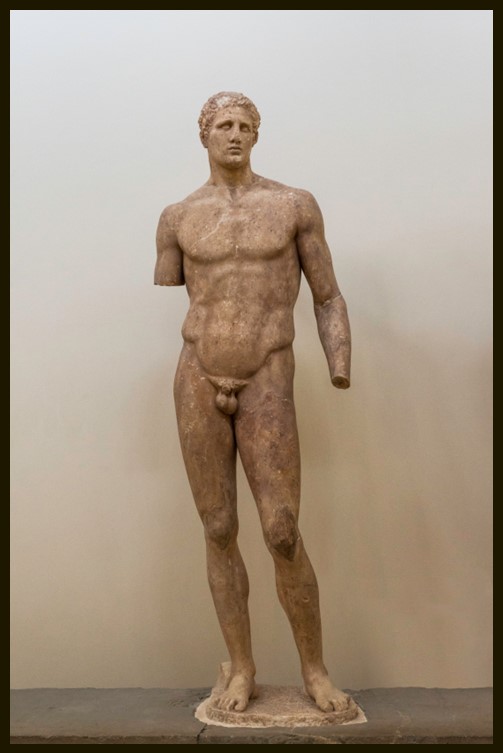
The statue of Agias son of Aknonios, and great-grandfather of Daochos II, is the Monument’s most preserved and most significant artwork. The Monument’s epigram, beneath his statue, identifies him as a distinguished athlete… Πρῶτος Ὀλύμπια παγκράτιον, Φαρσάλιε, νίκαις | Ἀγία Ἀκνονίου, γῆς ἀπὸ Θεσσαλίας, | πεντάκις ἐν Νεμέαι, τρις Πύθια, πεντάκις Ἰσθμοῖ · | καὶ σῶν οὐδεὶς πω στῆσε τρόπαια χερῶν… Man from Pharsalos (a town in Thessaly), having won the pankration first in Olympia, Agias, the son of Aknonios, from the land of Thessaly, (you won) five times in Nemea, three times the Pythian Games and five times on the Isthmos; no one has ever erected a victory monument at the expense of your poor.
As an athlete, Agias is depicted in a state of nudity, showcasing his athletic prowess as a victorious competitor. He is depicted standing upright, facing the viewer… but he appears restless! The weight distribution between his legs is not sharply differentiated. There is a lack of pronounced contrast between the weight-bearing, straight, right leg and the free, slightly bent, left leg. The statue appears to shift back and forth between the two stances, rather than standing at ease.
Equally restless seems to be the remaining body posture. The right hip, for example, juts out slightly, yet the overall impression is one of verticality. To the same extent, the arms are not ‘hanging’ down relaxed, but rather held slightly away from the athlete’s body, adding to their dynamic quality. The head, smaller in size compared to the statue’s size, rests on a muscular neck, slightly turning to the left. The facial details convey a sense of distinctive personality with a firmly set, sensual mouth, a rather large nose, and small eyes deeply set into the head. The gaze carried by Agias seems directed into space, imparting a certain detachment from the world. Overall, Agias’s torso, arms, legs, neck, and head, are powerfully built, but the body does not appear heavy. The son of Aknonios is a powerful Pankreatist, yet a tall, slender, elegant, thoughtful man.
Is the statue of Agias at Delphi the artistic creation of Lysippos, the great 5th-century sculptor from Sicyon?
According to modern scholars, Lysippos, the favourite sculptor of Alexander the Great, developed a particular artistic canon aimed at achieving specific effects. The statue of Agias, an idealized 4th century portrait, made long after the athlete’s death as part of the Monument of Daochos II, seems to ‘match’ Lysippos’ distinct artistic ‘effects’. It is characterized by a dynamic, yet ‘restless’ posture, a lean physique, individualized facial features, and a sense of detachment conveyed through the statue’s gaze.
The statue’s connection to Lysippos is further enhanced by an archaeological find at Pharsalos, the birthplace of Agias. A few years back, archaeologists unearthed the base of yet another statue of Agias (the actual statue is lost), which carried an inscription in part nearly identical to the Agias epigram at Delphi. It appears that the Delphi inscription was excerpted from that at Pharsalos, where, at its end, the name of Lysippos, the sculptor, was clearly written.
In conclusion…
The statue of Agias, part of the Monument of Daochos II at Delphi, was erected between the years 337/6 and 333/2 and embodies many artistic characteristics of the Lysippian style. The statue is identified as Agias, son of Aknonios, from an epigram inscribed on its base. This epigram is a copy of the inscription carved on the base of a chronologically older ‘statue’ of Agias discovered in the ancient city of Pharsalos, the birthplace of the athlete. The Pharsalos ‘statue’, commissioned, most probably, by Daochos II as well, believed to be an original creation of the sculptor Lysippos, done in bronze, and dated before 337/6 BC, has sparked many discussions about the creator of the statue of Agias at Delphi. Is it an original work by Lysippos or a copy of his bronze original statue at Pharsalos? Today, it is believed that the Delphic Agias, even if not a faithful replica of Lysippus’ original statue at Pharsalos, belongs to his workshop and, as a work from the 4th century BC, sheds light on the artistic trends of that era.
For a PowerPoint Presentation of the Monument of Daochos II in the Archaeological Museum at Delphi, please… Check HERE!
Bibliography: Rosina Colonia, The Archaeological Museum of Delphi, John S. Latsis Public Benefit Foundation, Athens, Greece (for the Statue of Agias and the Monument of Daochosin Delphi, go to pages 321-324) https://www.latsis-foundation.org/content/elib/book_13/delphoi_en.pdf and https://www.latsis-foundation.org/content/elib/book_13/delphoi_en.pdf and https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/artifact?name=Delphi%2C+Daochos+Monument%2C+Agias&object=Sculpture