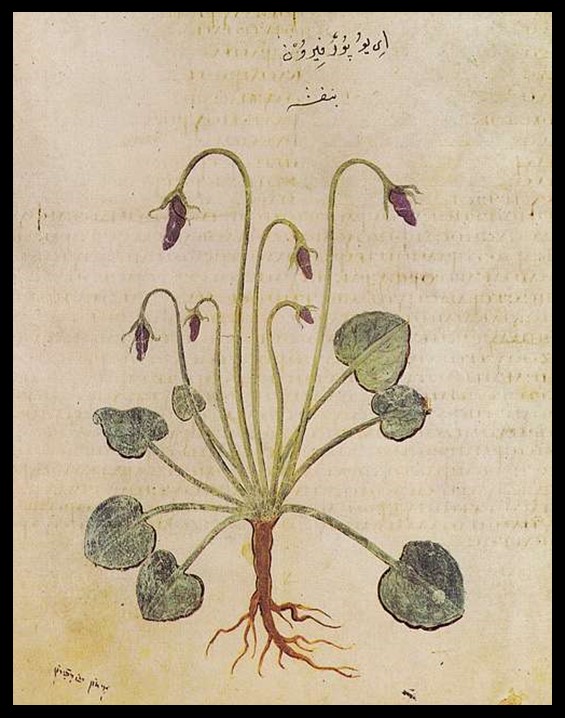
“The Vienna Dioscurides is a Byzantine Greek illuminated manuscript copy of “Medical Material” by Dioscorides, which was created in 515 AD. It is a rare surviving example of an illustrated ancient scientific and medical text… The original “De Materia Medica” or “On Medical Material” was first written between 50 and 70 CE by Pedanius Dioscorides. It is a pharmacopeia of medicinal plants and was widely read and used for more than 1,500 years… This specific manuscript copy was created in the Byzantine Empire’s capital, Constantinople, for the byzantine imperial princess, Anicia Juliana. She was the daughter of Anicius Olybrius, who had been one of the last Western Roman Emperors… The manuscript was presented to the princess in gratitude for her funding the construction of a church… The dedication miniature portrait of Anicia Juliana is the oldest surviving dedication portrait in a book…” I find it hard to encapsulate the manuscript’s significance more effectively. The Manuscript’s Folio 148 verso presenting Sweet Violet is my favourite! https://joyofmuseums.com/ancient-manuscripts-and-historically-influential-books/vienna-dioscurides/
This manuscript serves as one of my chosen ‘canvases’ for celebrating the arrival of each month. My goal for 2025 is to present twelve artworks—one for each month of the year—featuring exquisite depictions of flowers that beautifully convey their essence, symbolism, and historical importance. This initiative is more than just a tribute to flowers; it serves as a personal invitation to pause each month and appreciate the harmonious relationship between nature and art. Join us as we uncover how artists have woven the language of flowers into their work, using them to convey themes of love, purity, resilience, and more, allowing us to experience the beauty of each month in a fresh and vibrant way.
With a rich history spanning over two millennia, Sweet Violet is imbued with deep meaning and symbolism, making it a cherished choice for various occasions. As the flower of the month for February, its delicate fragrance and subtle beauty captivate the senses, while its association with love, modesty, and remembrance ensures that Sweet Violet remain a timeless floral favorite.
Sweet Violets (Viola odorata), known for their delicate fragrance and dainty blooms, have a storied history in botany that spans thousands of years. Originating in Europe and parts of Asia, they were among the earliest flowers to be cultivated for both medicinal and ornamental purposes. The ancient Greeks and Romans revered the Sweet Violet, using it in herbal remedies, perfumes, and even as a symbol of love and modesty. In medieval times, its medicinal properties were documented in early botanical texts, where it was praised for its ability to soothe headaches, respiratory issues, and inflammation. Renowned botanists, including Pedanius Dioscorides, highlighted the violet’s therapeutic virtues in works like De Materia Medica. Over the centuries, the Sweet Violet has maintained its place in botanical studies as a plant of both scientific and cultural significance, admired for its beauty, fragrance, and enduring symbolism.
The name Sweet Violet derives from its botanical classification, Viola odorata, which highlights both its genus and its defining characteristic—its fragrance. The genus name Viola is rooted in Latin, adopted from the ancient Greek word ion, which referred to violets and was associated with myths and poetic traditions. The epithet odorata translates to ‘fragrant’ or ‘sweet-smelling’ in Latin, emphasizing the flower’s delicate and appealing scent. In Greek mythology, violets were linked to figures like Io, a mortal transformed into a heifer by Zeus, for whom the gods caused violets to bloom as a food source. Over time, the name sweet violet became synonymous with modesty, purity, and love, encapsulating the flower’s gentle beauty and enduring fragrance.
Folio 148 verso of the Vienna Dioscurides features a stunning depiction of the Sweet Violet (Viola odorata), a testament to the manuscript’s masterful blend of scientific accuracy and artistic beauty. The page showcases the violet’s delicate blossoms, rendered in soft shades of purple and violet, with meticulous attention to the gentle curvature of the petals and the fine detail of the green leaves. The naturalistic portrayal reflects the Byzantine artists’ commitment to capturing the essence of the plant, both as a botanical specimen and as an object of aesthetic admiration. The composition is harmonious and balanced, with the violets depicted in their natural form, seemingly alive on the page. Beyond its visual appeal, the illustration exemplifies the manuscript’s role as both a practical pharmacopeia and a work of art, celebrating the beauty of nature through precise lines, subtle color palettes, and elegant simplicity. This folio, like many others in the Vienna Dioscurides, elevates the scientific depiction of plants to a level of timeless artistic achievement.
For a PowerPoint Presentation on the Vienna Dioscuridis, please… Check HERE!


















