
http://pompeiisites.org/en/archaeological-site/house-of-the-faun /
The House of the Faun is the grandest and most lavishly decorated private residence in ancient Pompeii. Originally serving as the home of a privileged family, this remarkable house, constructed in the latter part of the second century BC, circa 180 BC to be specific, occupied an entire city block and boasted an expansive interior spanning approximately 3,000 square meters. Home to many spectacular pieces of art, the House of the Faun stands out for its opulent floor mosaics, some of which remain in their original positions, while others are exhibited at the National Museum of Naples.
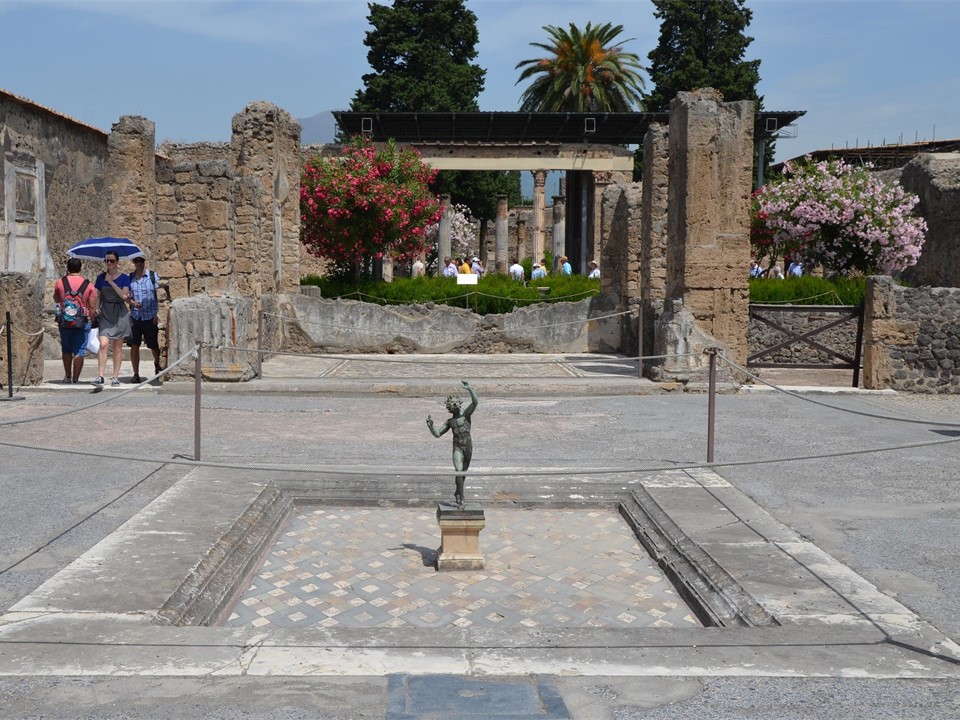

The title, House of the Faun, derived from an original bronze figurine portraying a dancing Faun situated at the heart of a white limestone Impluvium (Plan No. 27), a basin for collecting water. Fauns, ethereal beings associated with untamed forests, were frequently linked by Romans to Pan and Greek satyrs, who were followers of Dionysus, the Greek deity associated with wine and agriculture. The original bronze statuette of the Dancing Faun is in the National Museum of Naples, thus the statue seen in the house’s ruins today is a copy.
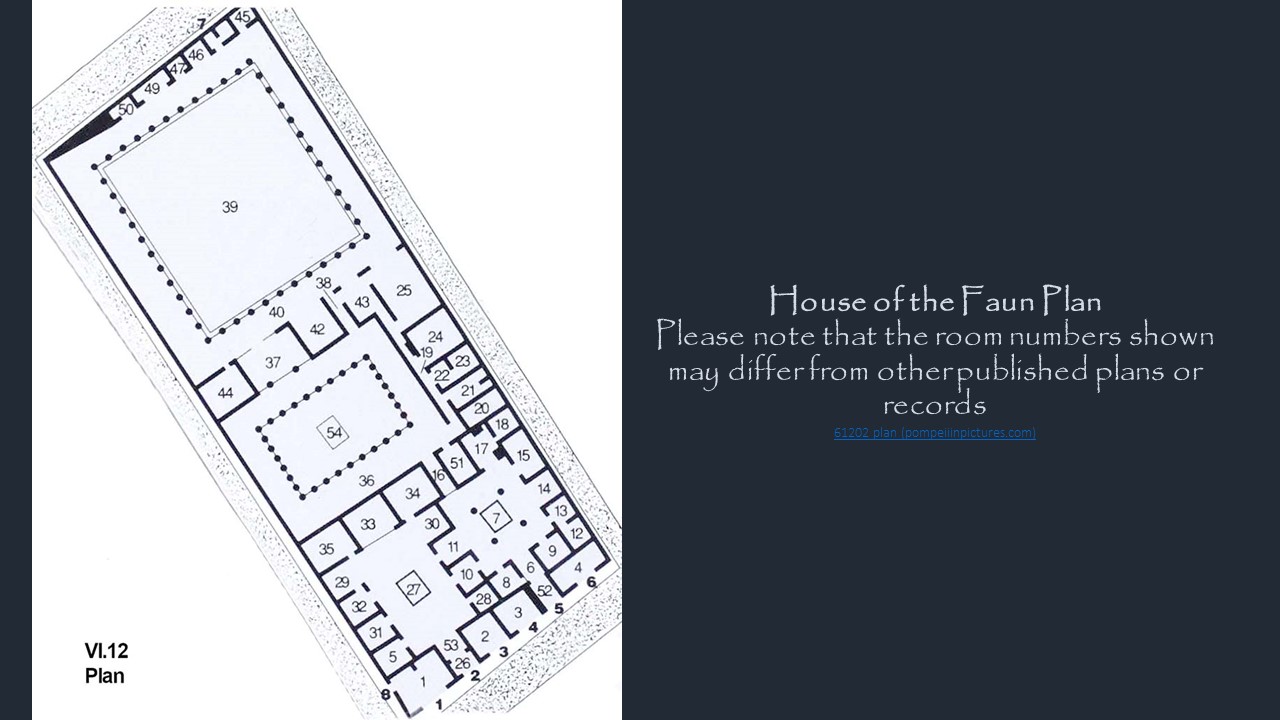
The elaborate and sophisticated architectural plan of the House of the Faun reflects the wealth and social status of its occupants and follows the standard Roman architectural style of a Domus (private family house) but on an exceptionally grand scale. The House had, for example, two main Entrances, (Plan No 2bold and No 5bold). The principal Entrance (Plan No. 2bold) led to the Tuscan Atrium (Plan No. 27), while a secondary Entrance (Plan No. 5bold) led directly to the Tetrastyle Atrium (Plan No. 7) and the service areas. The Tuscan Atrium, with a large open hall, the heart of the house, had the impluvium in the center, a basin that collected rainwater, with a small bronze statue of a Dancing Faun, giving the house its name.
Around the Tuscan Atrium were various rooms including cubicula (bedrooms), a tablinum (office or study), and triclinia (dining rooms). A special room, the Exedra (Plan No. 37), was off the smaller Peristyle (Plan No. 36) and contained the famous Alexander Mosaic.

The house had two Peristyles (Plan No. 36 and No. 39) or colonnaded courtyards. The larger one (Plan No. 39), was essentially a garden surrounded by a colonnade. The second smaller Peristyle (Plan No. 36) was more private and was linked to the private living areas. Separate service quarters were attached to the secondary entrance and the Tetrastyle Atrium (Plan No. 5bold and No. 7). These included the kitchen, a small bathing complex, slave quarters, and storerooms. On the exterior, the house had tabernae or shops (Plan No. 1, No 2, No 3, and No 4). These were leased out to generate additional income.
The House of the Faun represents a clear example of how the Romans valued both private and social aspects of life, and how they incorporated this into their architecture.
This residence is most famous for its intricate and beautifully preserved mosaics, which not only demonstrate the wealth and status of its inhabitants but also provide an insight into the aesthetic tastes of the Roman elite during this period. The mosaics serve as invaluable examples of the ancient Roman mosaic tradition, each one unique in design and execution.
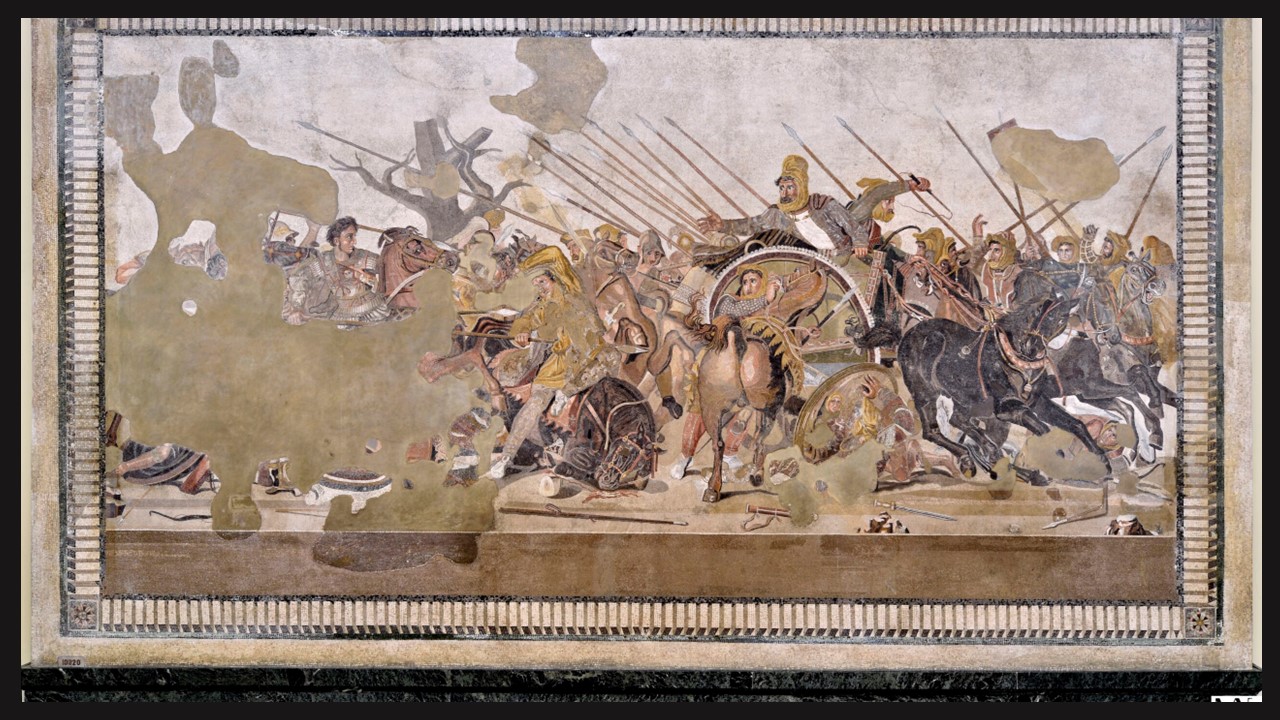
The most famous mosaic found in the House of the Faun is the Alexander Mosaic, which covered the floor of the Exedra (Plan No. 37). The mosaic, dated during the 2nd century BC, is believed to depict the Battle of Issus (333 BC) between Alexander the Great and Darius III of Persia. The mosaic is lauded for its attention to detail, dramatic energy, and sophisticated use of perspective, showcasing a high degree of artistic skill.
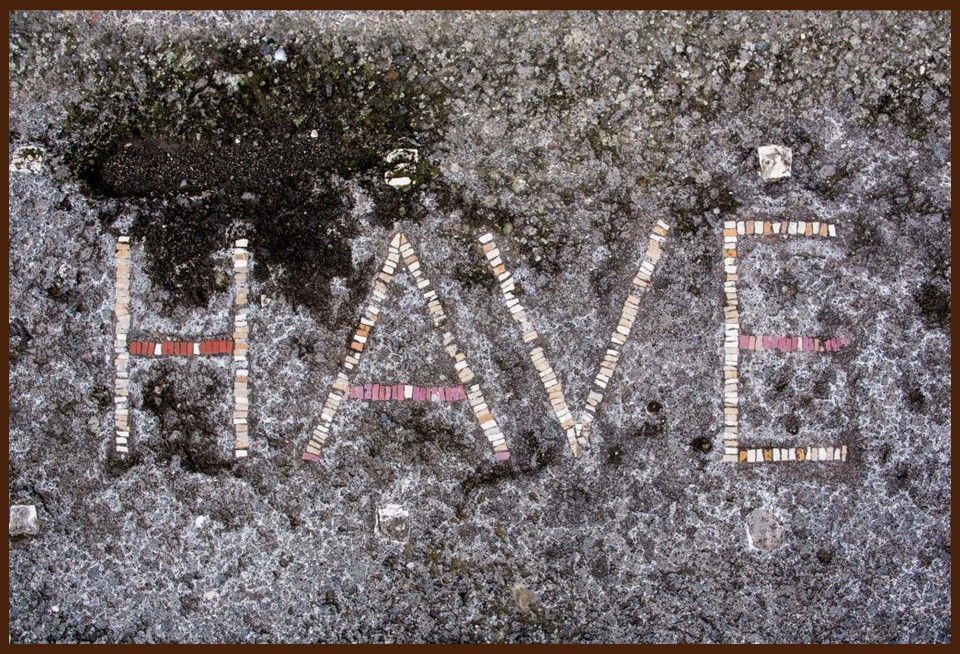
The mosaic I find particularly touching presents one word only. It was placed in front of the main entrance to the House (Plan No. 2bold), reading HAVE, a Latin word meaning ‘Greetings’ or ‘Welcome’. Isn’t it a particularly welcoming touch to the grandeur of this spectacular Pompeiian house?

The PowerPoint I prepared for my new BLOG POST the House of the Faun has two Parts. The first consists of photos of the House itself. The second part of the PowerPoint presents photos of its famous Mosaics. For the PowerPoint, please… Check HERE!
This Video dedicated to the House of Faun is worth seeing… https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-X4i0psJ2p0