Oaks, Washington, DC, USA
http://museum.doaks.org/objects-1/info/27455
It was but recently the whole human race celebrated various ten-year periods for the great Emperor with festive banquets. It was but recently we ourselves hymned the conqueror with praises for his twenty years, taking the floor at the Council of God’s ministers. Just now we wove garlands of words also for his thirty years, in the very palace hardly yesterday to crown his sacred head. But today our thought stands helpless, longing to express some of the conventional things, but at a loss which way to turn, stunned by the sheer wonder of the amazing spectacle. Wherever it casts its gaze, whether east or west, whether all over the earth or up to heaven itself, every way and everywhere it observes the Blessed One present with the Empire itself… writes Eusebius PamphiliOn the Life of the Blessed Emperor Constantine back in the 4th century AD. Today, celebrating Emperor Constantine’s Name-Day, I present you a Triptych Leaf with St. Constantine from the Dumbarton Oaks Collection and wish every person named Constantine or Constantina… Health, Happiness, and Prosperity! http://archive.eclass.uth.gr/eclass/modules/document/file.php/SEAD260/%CE%95%CF%85%CF%83%CE%AD%CE%B2%CE%B9%CE%BF%CF%82%2C%20Life%20of%20Constantine%20%28trans.%20Averil%20Cameron%20-%20Stuart%20Hall%29.pdf
Emperor Constantine is often described as the most important emperor of Late Antiquity. His political and military acumen, foresight, and sagacity mark his rule as a significant pivot point between Ancient History and the Middle Ages. His reign was eventful and brutal, but his momentous decisions created a whole new world for Europe and parts of the Eastern Mediterranean… He legalized and supported Christianity, and he founded the “New Rome,” mythical Constantinople, the city that ruled supreme in beauty, and power, for a thousand years! Emperor Constantine, while alive, was revered and feared at the same time. He was the greatest of statesmen… he became a Saint of the Christian faith, and a shining example for Emperors to come into the world! https://www.nationalgeographic.com/culture/article/constantine
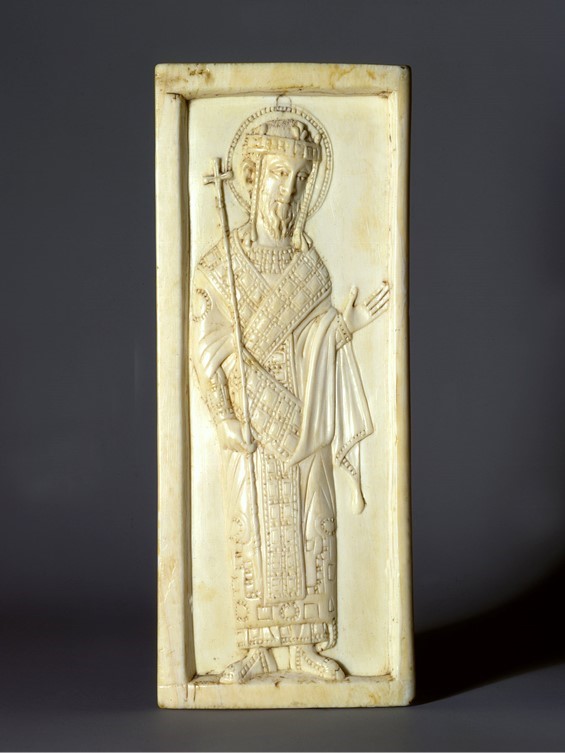
Originally in the Collection of the famed connoisseur of European paintings and of objects of fine art from many cultures, Count Grigory Sergeievich Stroganoff (1829-1910) of Rome, Paris, and St Petersburg, the Triptych Leaf with St. Constantine entered the Dumbarton Oaks Collection in 1947. The small ivory representation of a Saint dressed in Imperial attire, a loros wrapped around his body and a crown with pendilia, is identified with Emperor/Saint Constantine I (208?-337 AD). Along with his mother St. Helena, according to John Hanson of Dumbarton Oaks, also dressed in royal robes, these saints were often shown flanking a representation of the True Cross. In all probability, this is the case for the Dumbarton Oaks Ivory panel. It was the left-wing of a precious triptych.. http://museum.doaks.org/objects-1/info/27455
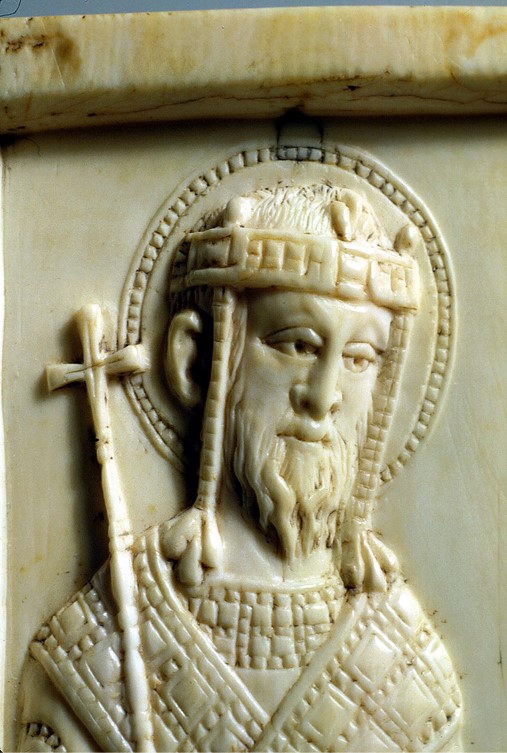

http://museum.doaks.org/objects-1/info/27455
There were no less than eleven Byzantine Emperors by the name of Constantine, the number rising to twenty-two if children and relatives with little or no independent power were added to the list. They all wanted to connect with the Empire’s founder and share his legacy. It is perhaps for this reason that the saint’s features resemble, as stated by John Hanson, the facial features of early 10th century Byzantine Emperors, the time when the Triptych Leaf with St. Constantine was created. If the identity of the emperor was specifically Constantine VII Porphyrogennetos, the resemblance creates a complex sign of authority and sanctity, aligning the living emperor with his imperial namesake. https://www.persee.fr/doc/numi_0484-8942_2005_num_6_161_2594 and http://museum.doaks.org/objects-1/info/27455
For a Student Activity on the Triptych Leaf with St. Constantine, please… Check HERE!