https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/statue-kore-kore-chios
Kallos, according to the Museum of Cycladic Art experts, is an ideal developed in ancient Greek thinking and was expressed through the verses of the epic (8th century BC) and lyric (7th – 6th century BC) poets, initially as outward beauty. From the sixth century BC onwards, the concept was crystallized gradually through the texts of the philosophers, who referred to Kallos as a combination of physical appearance and virtues of the soul. It is on this dimension of Kallos that the exhibition of the Museum of Cycladic Art concentrates, enhancing the contribution of ancient Greece to defining the notion of beauty that prevails to this day. “Κάλλος” The Ultimate Beauty is a must-see Exhibition in the Museum of Cycladic Art in Athens running from 29/09/2021 until 16/01/2022. “Κάλλος” and the Kore from Chios is my new BLOG POST inspired by this wonderful Exhibition… focusing on a unique exhibit from the Acropolis Museum in Athens. https://cycladic.gr/en/page/kallos-i-ipertati-omorfia and https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/statue-kore-kore-chios
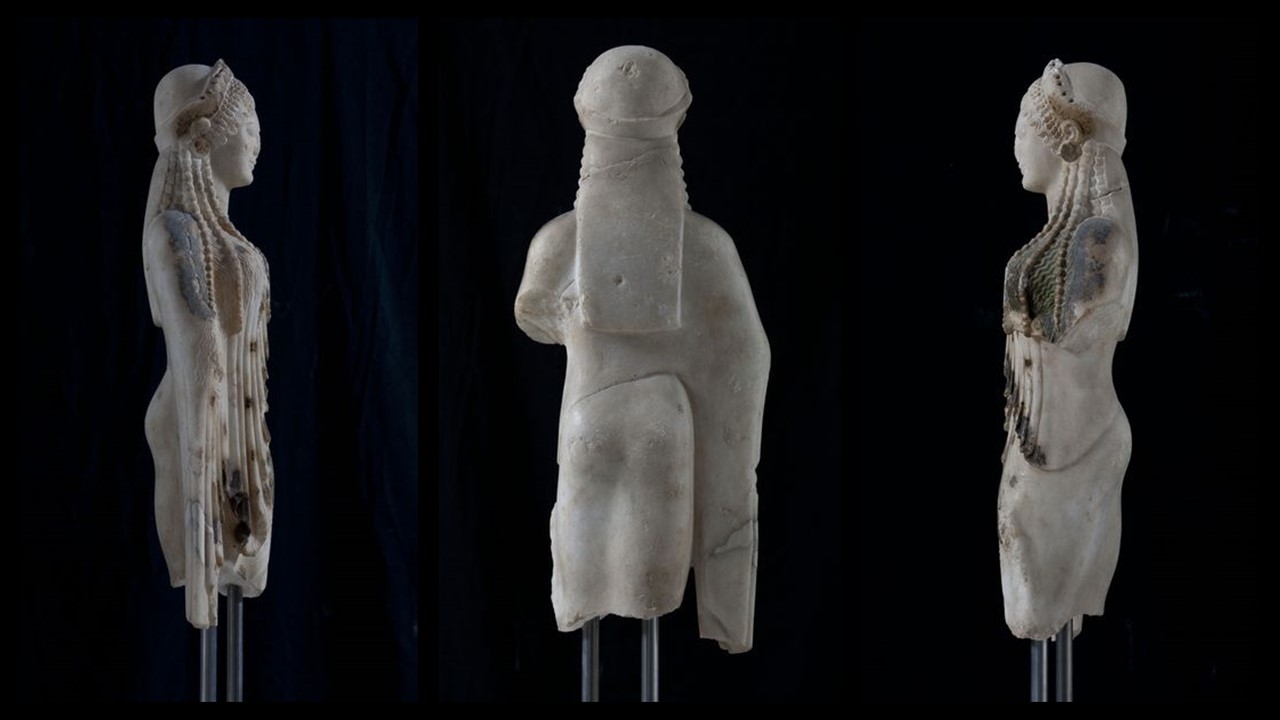

https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/statue-kore-kore-chios
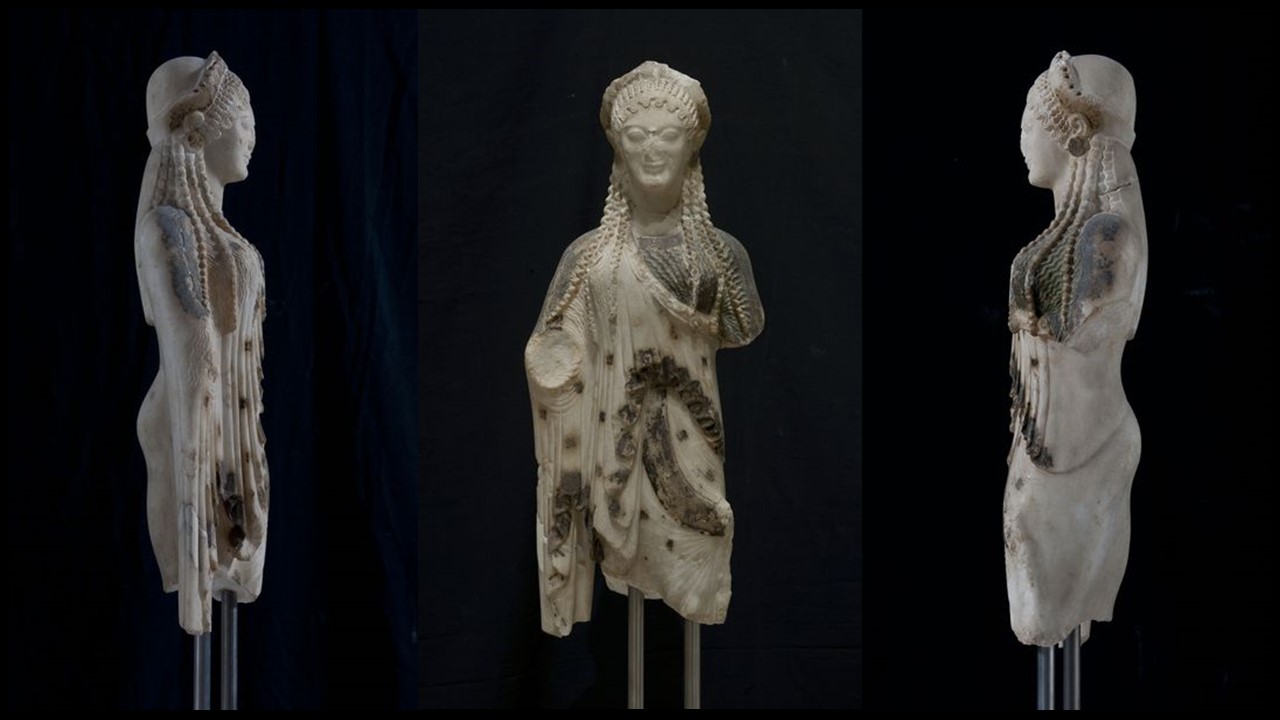
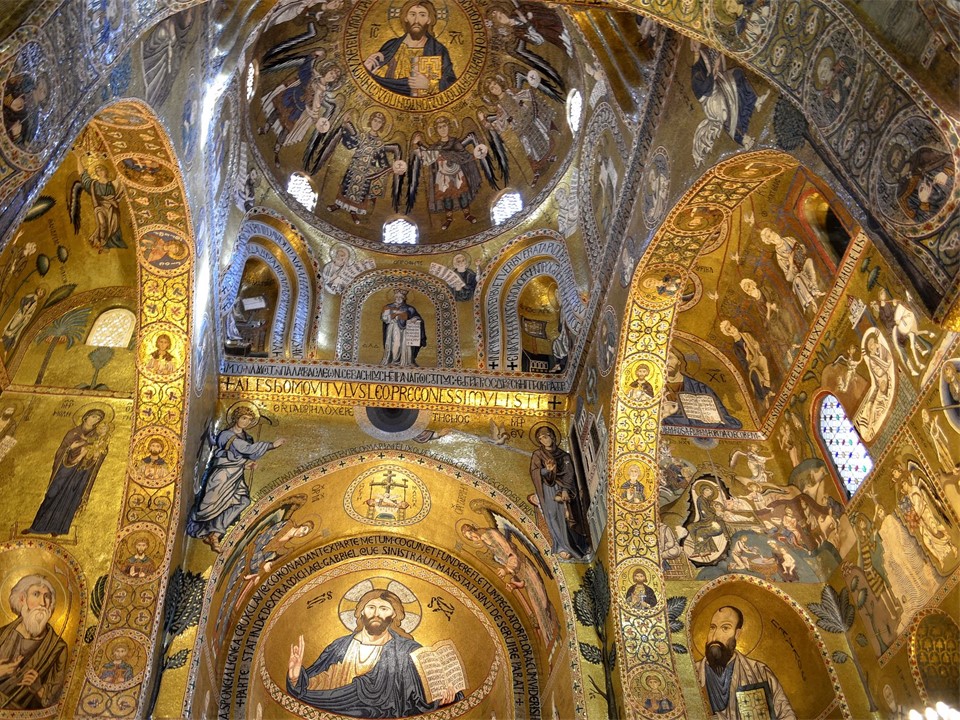
The Kore from Chios is one of the most impressive Kore excavated on the Acropolis of Athens back in the late 19th century, part of the Perserschutt, the numerous remains of statues vandalized by the Achaemenids during the terrible years of the second Persian invasion… Ten years after the Battle of Marathon (490 BC), the Persians returned to Greece and after their victory at the Battle of Thermopylae, in September of 480 BC, they entered Athens. The small number of Athenians who had barricaded themselves on the Acropolis, hoping that the Wooden Walls of the Delphic Oracle will protect them, were eventually defeated, and Xerxes ordered Athens to be torched. Those Persians who had come up first betook themselves to the gates, which they opened, and slew the suppliants; and when they had laid all the Athenians low, they plundered the temple and burnt the whole of the acropolis. (Herodotus VIII.53). Months later, after the victory at Salamis, and the Battle of Plataea in 479 BC, the Athenians returned to their city… they respectfully buried the mutilated sacred statues of the Archaic period on the Acropolis and proceeded with reorganizing their civic and private lives… waiting for the right time to rebuild their Acropolis. https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/special-topics-art-history/arches-at-risk-cultural-heritage-education-series/xa0148fd6a60f2ff6:ruins-reconstruction-and-renewal/a/destruction-memory-and-monuments-the-many-lives-of-the-parthenon
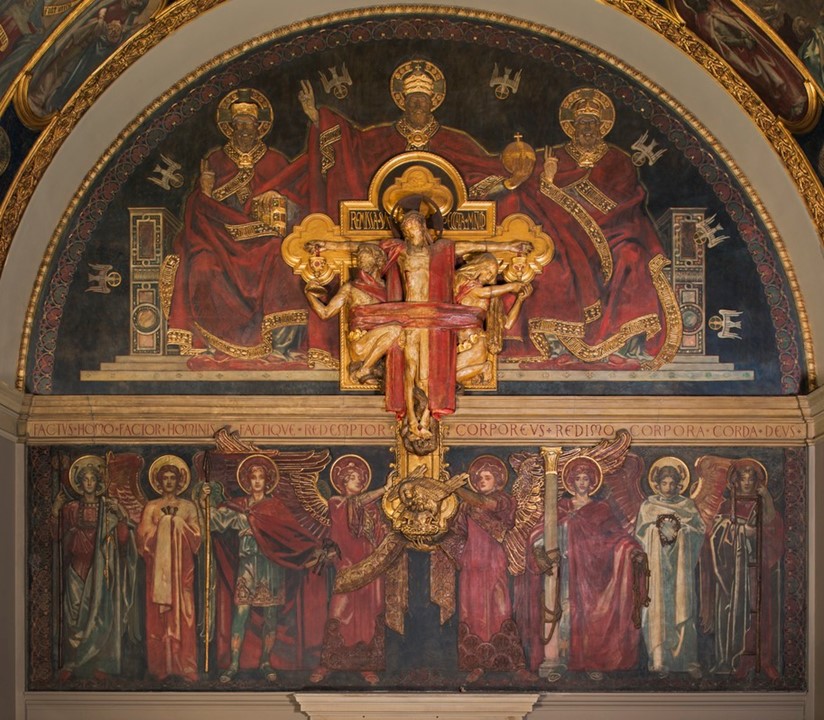
In 1886, excavating the Perserschutt deposits, archaeologists discovered the head of the Kore from Chios east of the Parthenon while its body was discovered in 1888 south of the Parthenon temple. The “Chiotissa” as it is affectionately called by the Greeks, is an Archaic period (c. 600-480 BC) Kore, whose artist was most probably from the Aegean island of Chios. Statues of a Kore, plural korai, refer to a type of freestanding effigy of a maiden. Kore is a draped female figure—carved from marble and originally painted—standing erect with feet together or sometimes with one foot, usually the left, slightly advanced. The arms are sometimes down at the sides, but in most cases, one is brought up closely across the front of the body or is extended, holding an offering; the other is lowered, often clasping a fold of drapery. In the earliest korai, the bodies are so blocklike that they hardly seem to represent feminine form… Later, the drapery became more fluid, with a greater variation in the folds gained by having one hand of the kore pull the drapery tightly across thighs and buttocks. The garments worn by the kore figures changed in style as well, displaying a pattern, either on borders or as single ornaments scattered over larger areas. https://www.britannica.com/art/kore-Greek-sculpture, https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/statue-kore-kore-chios. You can also check BLOG POST Daughters of Eleutherna https://www.teachercurator.com/art/daughters-of-eleutherna/

https://cycladic.gr/en/page/kallos-i-ipertati-omorfia
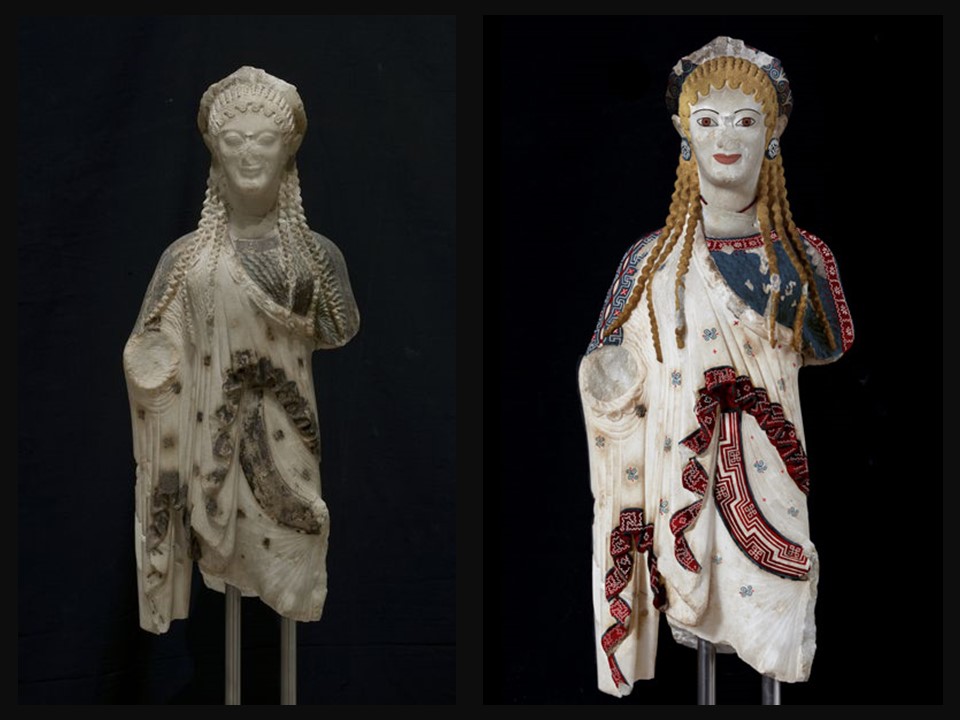

My life and fortunes are a monstrosity, partly because of Hera, partly because of my beauty. If only I could shed my beauty and assume an uglier aspect, the way you would wipe color off a statue… by Euripides, Helen, 260-263. (Translated by R.Kannicht, Heidelberg 1969) https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/statue-kore-kore-chios
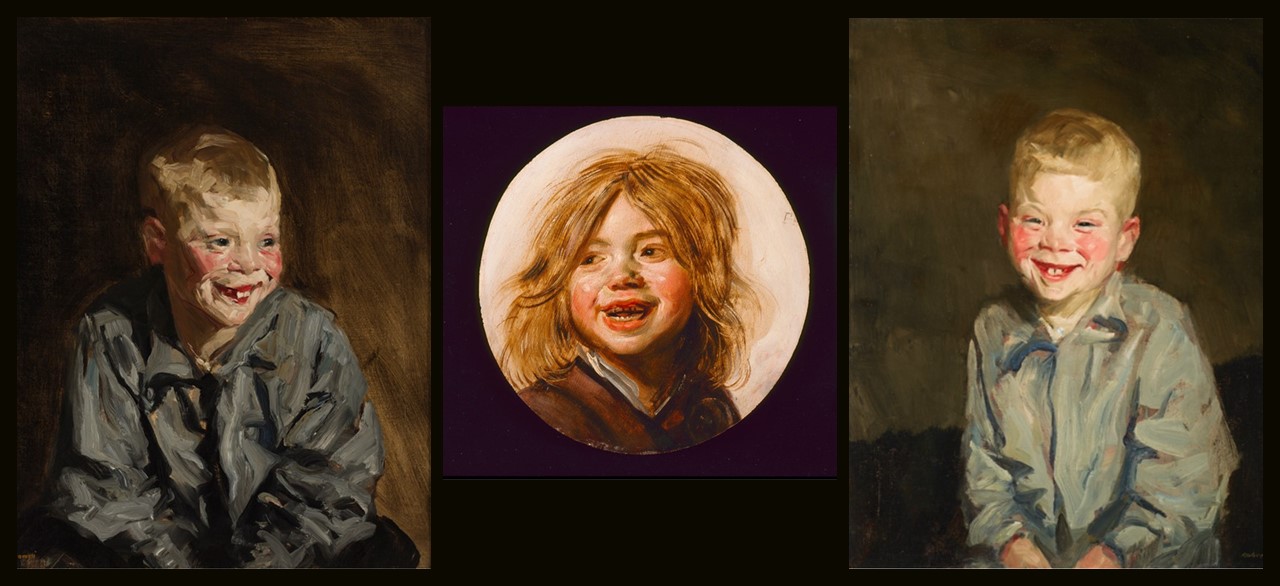
The Kore from Chios is small in size but impressive in… Κάλλος! Created by a fine Eastern Greek sculptor… maybe the grandson of Archermos of Chios, the fine-looking “Chiotissa,” is depicted stepping slightly forward pulling her skirt to the side with her left arm, creating thus, a fan of fine radiating folds. She wears the Ionian style of dress… a fine, crinkly chiton over which a short himation is draped diagonally. The carving is richly detailed, the paint even more so. The chiton is blue, the himation edged with a red and blue design, the Stephane was decorated with a Maeander, the earrings and a necklace painted, and the hair colored as well. I look at her and remember Eleni, Euripides’s heroine… My life and fortunes are a monstrosity, partly because of Hera, partly because of my beauty. If only I could shed my beauty and assume an uglier aspect, the way you would wipe color off a statue… http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/artifact?name=Athens%2C+Acropolis+675&object=Sculpture and https://www.greece-is.com/the-colors-of-antiquity/
For a Student Activity on the Kore from Chios, please… Check HERE!