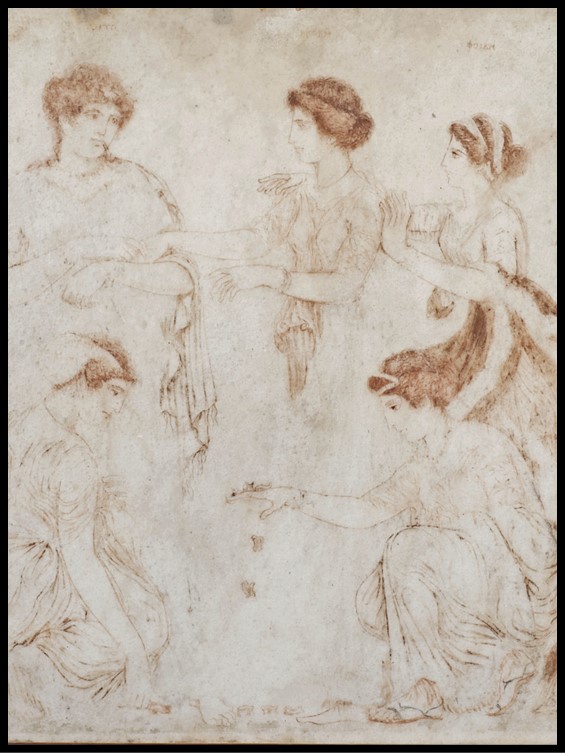
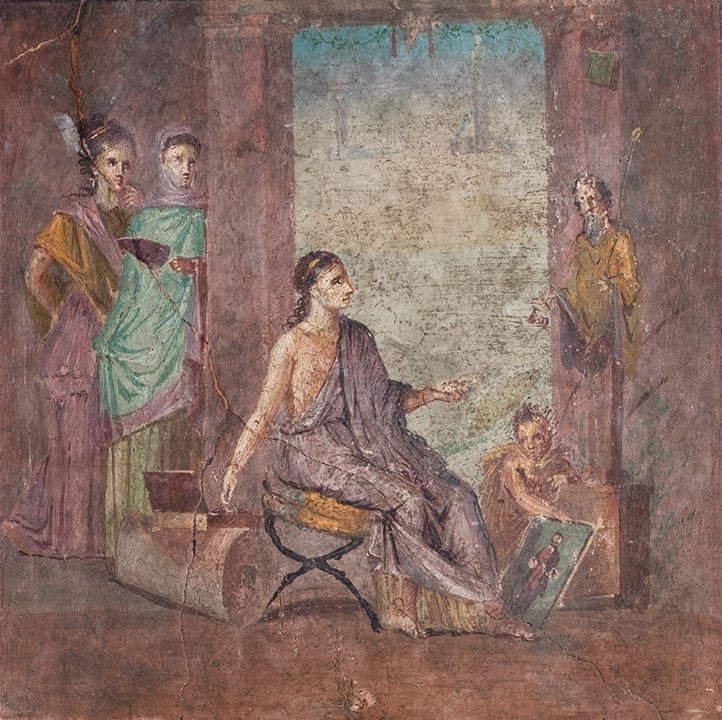
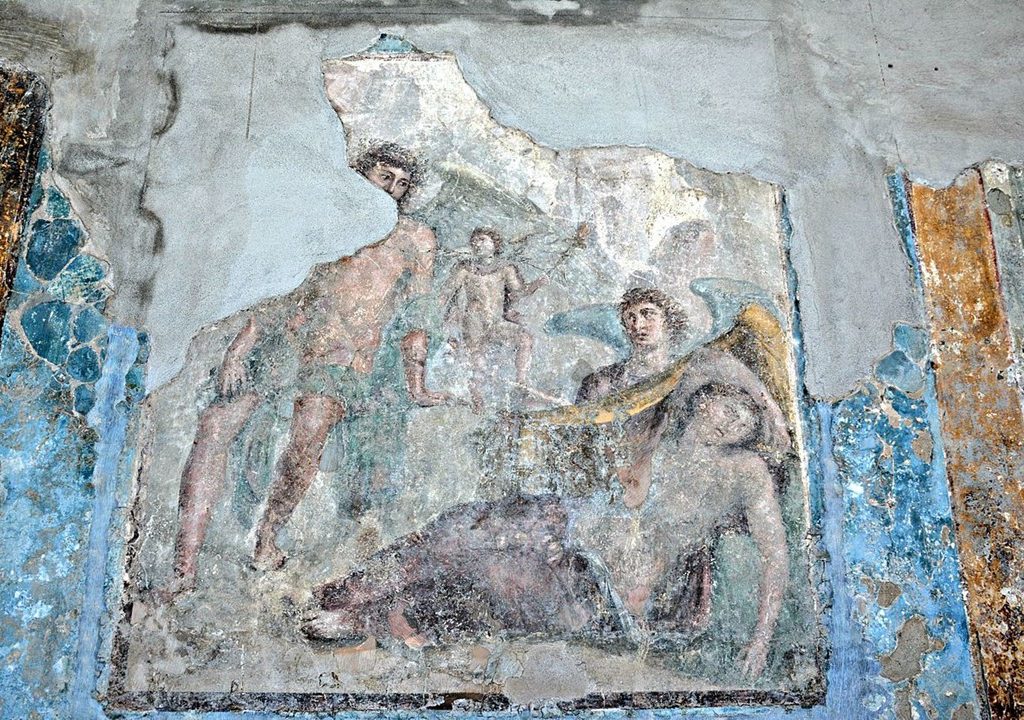
Astragaloi players from Herculaneum, 1st cent BC-1st cent AD, Marble and Pigment, 47.6×50.5 cm, National Archaeological Museum of Naples, Italy https://mann-napoli.it/affreschi/#gallery-8
Niobe ((P. Ovidius Naso, Metamorphoses)… So many things / increased her pride: She loved to boast / her husband’s skill, their noble family, / the rising grandeur of their kingdom. Such / felicities were great delights to her; / but nothing could exceed the haughty way / she boasted of her children: and, in truth, / Niobe might have been adjudged on earth, / the happiest mother of mankind, if pride / had not destroyed her wit… and Leto’s anger fell hard on her… Childless— she crouched beside her slaughtered sons, / her lifeless daughters, and her husband’s corpse. / The breeze not even moved her fallen hair, / a chill of marble spread upon her flesh, / beneath her pale, set brows, her eyes moved not, / her bitter tongue turned stiff in her hard jaws, / her lovely veins congealed, and her stiff neck / and rigid hands could neither bend nor move.— / her limbs and body, all were changed to stone… The Astragaloi Players, the painted marble Pinax from Herculaneum, takes the viewer to moments of contentment when Leto and Niobe certainly they loved each other like true friend (Sappho Fragment 142)… before Niobe’s Ύβρις (transgression against a god) and Leto’s painful Wrath! https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.02.0028%3Abook%3D6 and https://digitalsappho.org/fragments/fr118-168/
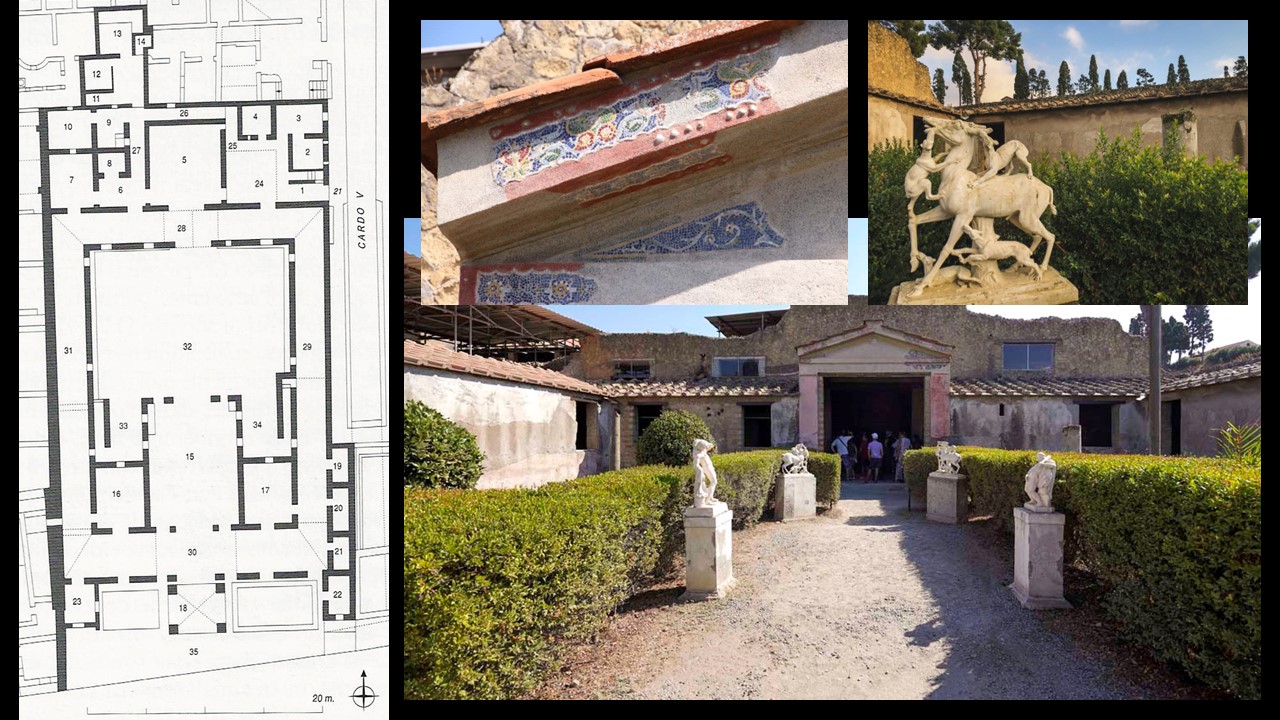
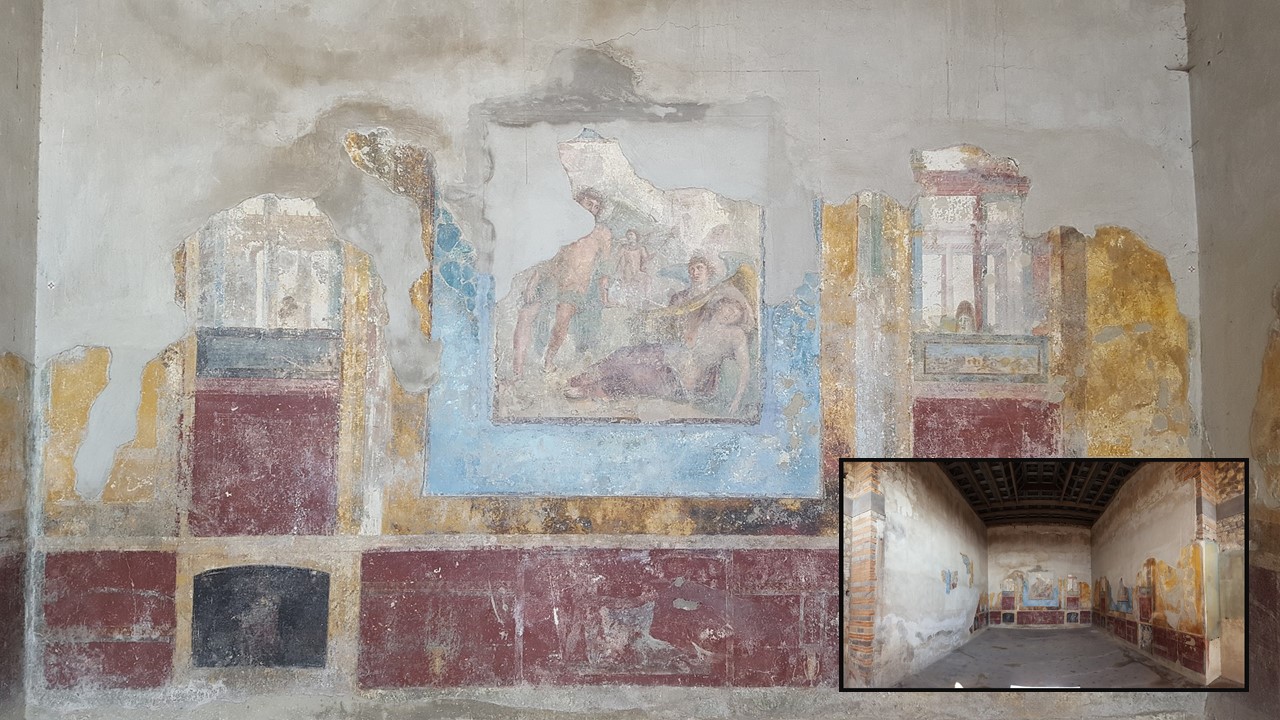
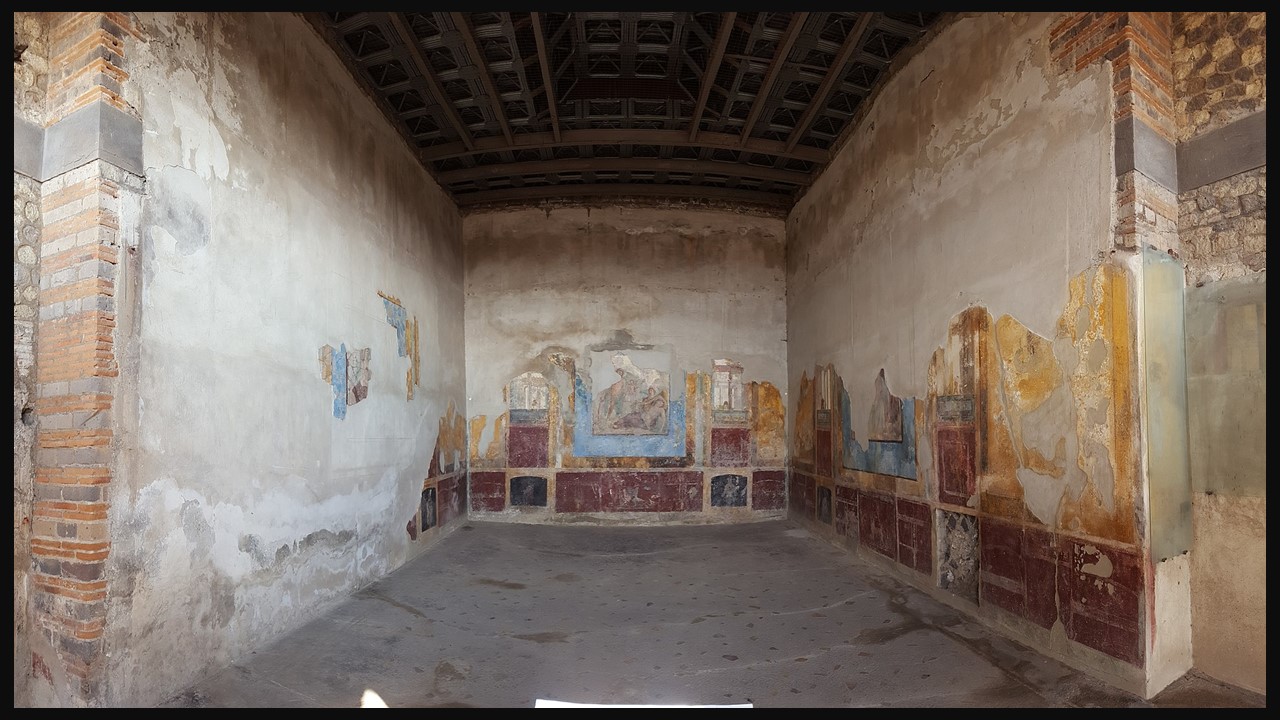
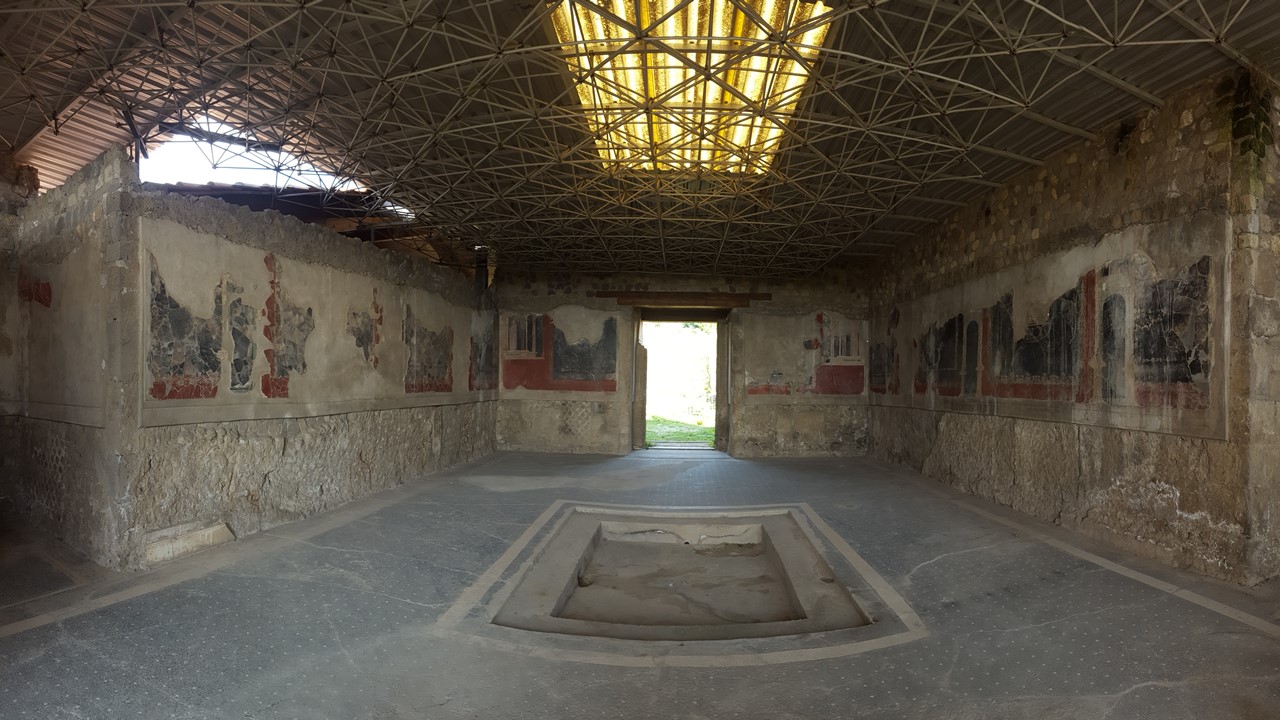
The famous painting of the Astragaloi Players was discovered in the House of Neptune and Amphitrite, in Herculaneum, on Cardo IV, in May 1746. Not one of the largest houses in ancient Herculaneum, yet one of the most famous, and visited, as it boasts three masterpieces.
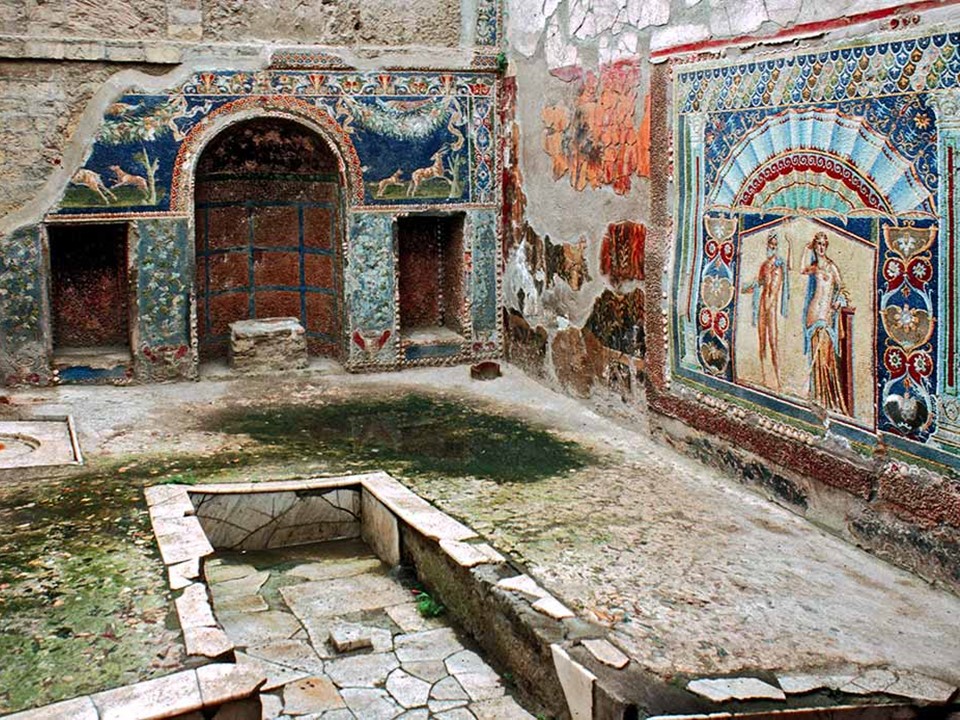

First, the mosaic decorating the Nymphaeum, located in the Inner Garden Court of the house. Adorned with geometric and floral motifs and hunting scenes with dogs and deer composed of glass paste tesserae, shells, and designs of mother of pearl, the Nymphaeum mosaic is brightly colorful and elegant. Second, in the center of the east wall, the mosaic after which the house is named shows Neptune and Amphitrite surrounded by an exquisite frame of decorative motifs. Third, the Marble Pinax of the Astragaloi Players is detached and exhibited today in Naples Archaeological Museum.
The depicted scene in the marble Pinax, titled Astragaloi Players, presents the act immediately preceding the massacre of the Niobids. The myth, also told by Ovid (Metamorphoses, VI), narrates that Niobe, wife of Amphion, king of Thebes, and mother of many children, dared to declare herself even superior to the goddess Leto, mother of only two children, Apollo, and Artemis. Leto, angered by Niobe and her outrageous presumption, ordered the killing of the queen’s seven sons by Apollo and the killing of her seven daughters with arrows shot by Artemis. https://mann-napoli.it/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/10.-Giocatrici-di-astragali.pdf

https://herculaneum.uk/Ins%205/Herculaneum%205%2007.htm
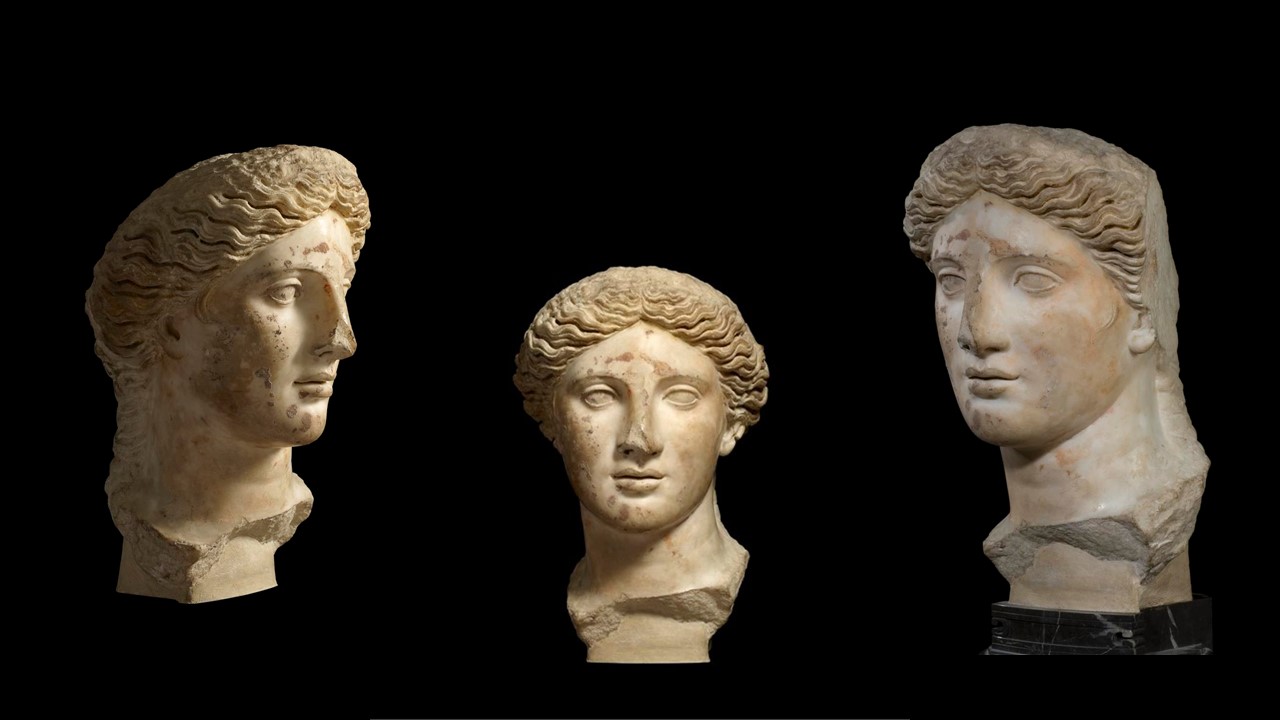
The inscriptions in capital Greek characters, placed next to each figure depicted in the Pinax, identify the members of the story by name. In the background, three women are identified as Leto (left), Niobe (middle), and Phoebe (right). In the foreground, kneeling and involved in a game of Astragaloi, the artist of the composition placed two of Niobe’s daughters, Aglaia (left) and Ilaria (right). Another inscription, placed in the upper left corner, introduces us to the artist, a man called Alexander from Athens (ΑΛΕΞΑΝΔΡΟΣ ΑθΗΝΑΙΟΣ ΕΓΡΑΦΕΝ).
Antonio Coppa of the Naples Archaeological Museum believes that this marble painting is most likely a Neo-Attic remake of an original painting of the late 5th century BC, attributable to the famous Zeuxis. The archaeologist also believes that the presence of names identifying each figure depicted in the composition fits into the archaizing fashion of the Augustan age, allowing to date the work between the end of the 1st century BC and the beginning of the 1st century AD. https://mann-napoli.it/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/10.-Giocatrici-di-astragali.pdf
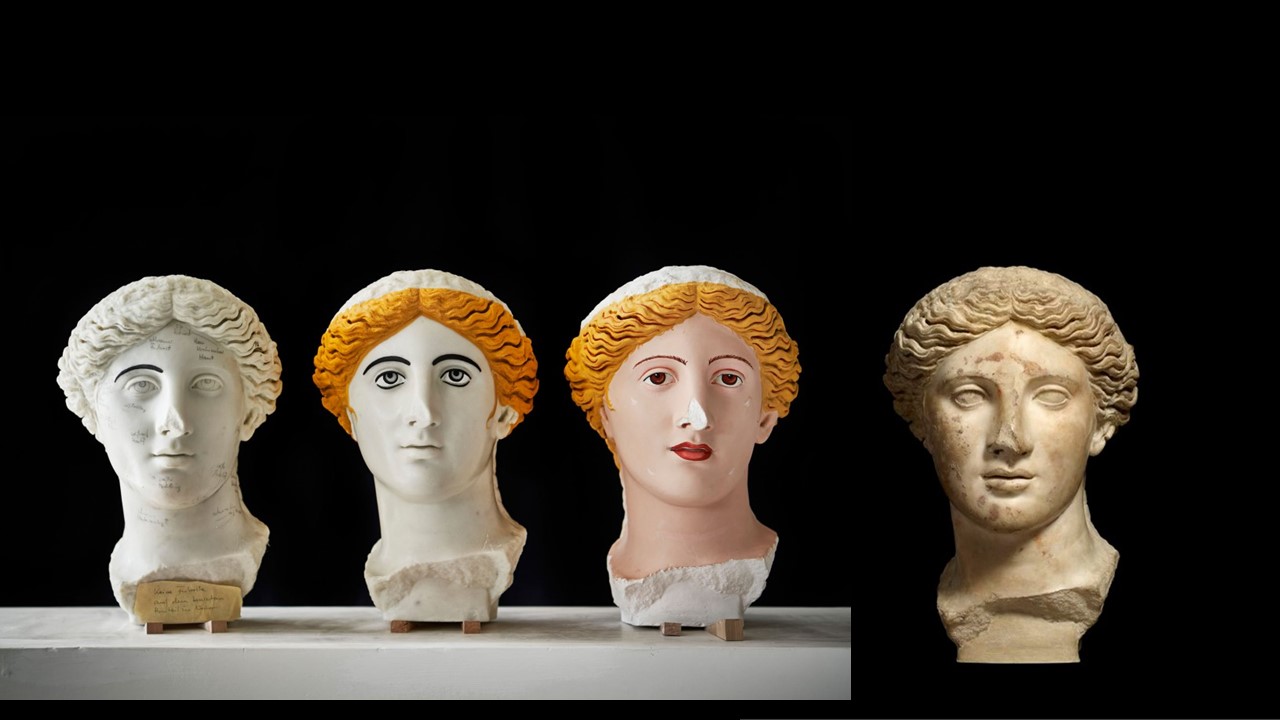
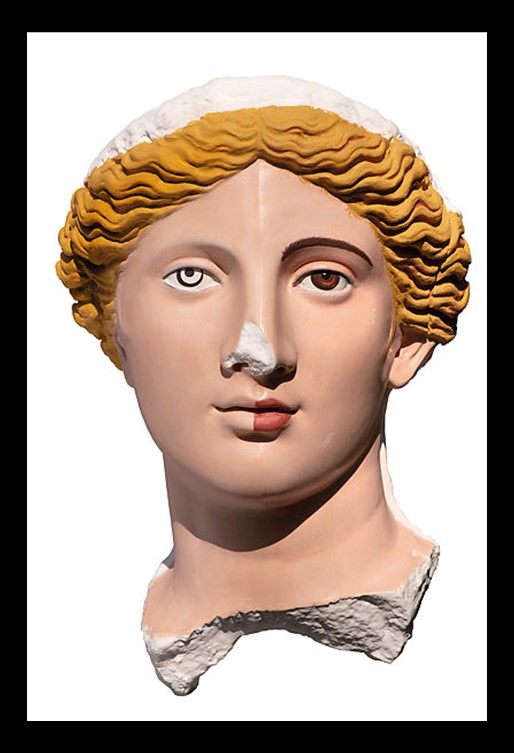
The painting of the Astragaloi Players was immediately defined as “monochrome”, believing it to be an example of those paintings in which the only color for their realization was the cinnabar. However, recent investigations into the picture pigment have highlighted the use of multiple colors: pink and yellow for the clothes, red for the sandals, and black for the hair; moreover, the different gradations of color gave volume to the figures, therefore the current monochrome is only the result of the action of time. https://mann-napoli.it/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/10.-Giocatrici-di-astragali.pdf
What a magnificent discovery!
For a Student Activity, please… Check HERE!